Obesity is not only causes by eating more and moving less. But if it were that simple, long term weight loss wouldn’t be so difficult. The truth is, hormones not just calories play a central role in weight gain. Two of the most important hormones involved are insulin and leptin. When the body becomes resistant to these hormones, fat gain becomes easier and weight loss becomes harder. Let’s explore how this works.
Is Insulin Causing Your Weight Gain?
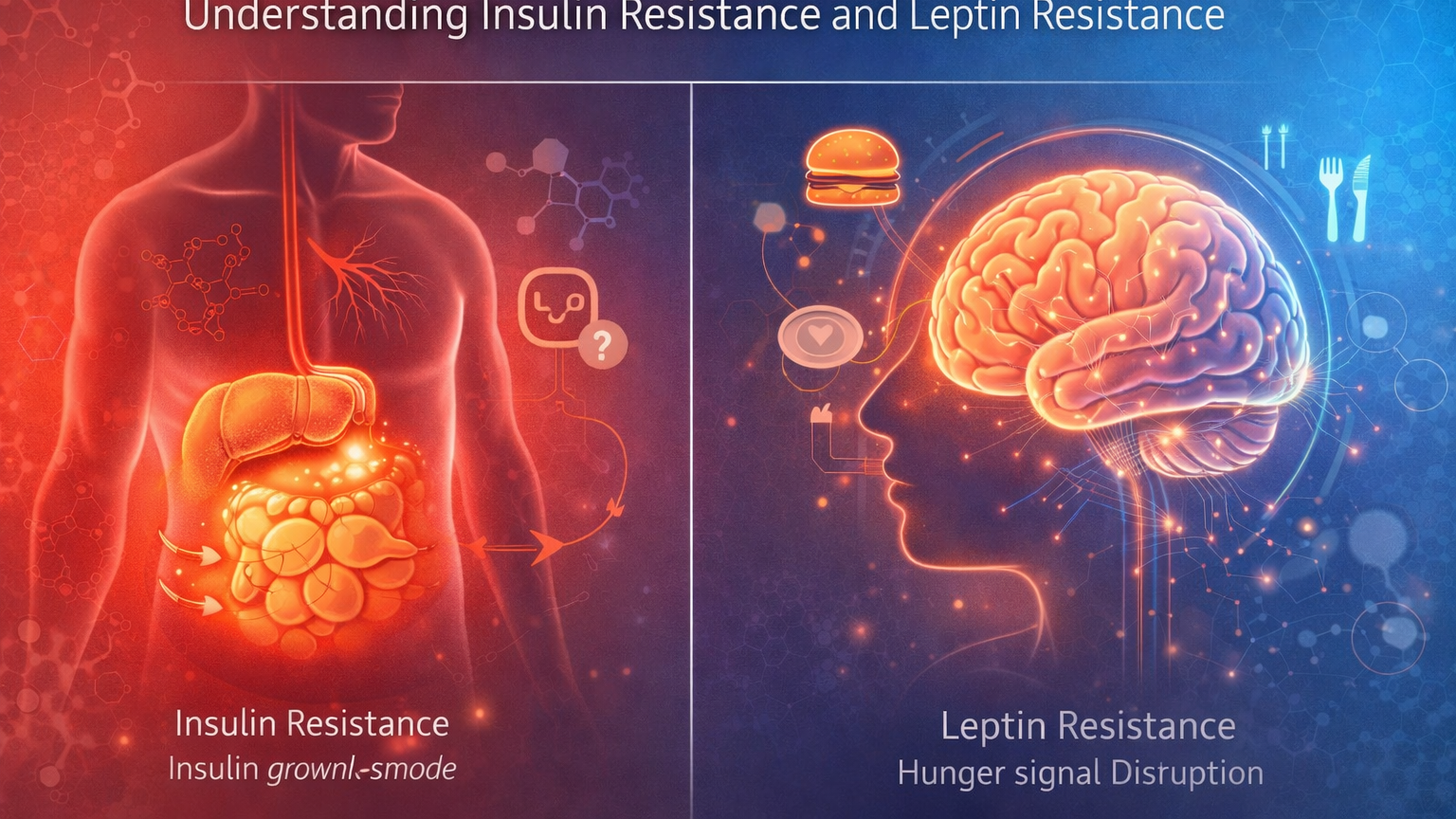
The Science Explained Insulin is released by the pancreas whenever you eat, especially carbohydrates. It's main job is to move glucose from your bloodstream into your cells for energy.
But insulin has another powerful function: It signals your body to store fat. When insulin levels remain elevated for long periods due to frequent eating, refined carbs, stress, or poor sleep cells begin to ignore its signal. This condition is known as insulin resistance.
What happens during insulin resistance?
The body produces even more insulin Fat storage increases (especially abdominal fat) Blood sugar levels fluctuate Cravings and energy crashes become common High insulin keeps the body in storage mode, making fat burning difficult.
Leptin Resistance and Weight Gain: Understanding the Hunger Hormone Leptin is produced by fat cells and communicates with the brain to regulate hunger and metabolism.
Its job is simple: You have enough stored energy. Stop eating. However, when fat mass increases, leptin levels rise continuously. Over time, the brain stops responding properly to leptin’s signal. This is called leptin resistance.
What happens during leptin resistance? Constant hunger Difficulty feeling full , Slower metabolism , Increased fat storage Even though leptin levels are high, the brain acts as if the body is starving.
Which Hormone Drives Obesity First?
Research suggests that insulin resistance often develops first. Here’s the typical sequence: Frequent high insulin levels promote fat storage. Fat cells expand and produce more leptin. Chronic high leptin leads to leptin resistance. Both hormonal systems become dysregulated. At this stage, weight gain accelerates and weight loss becomes extremely difficult.
In short: Insulin resistance promotes fat gain. Leptin resistance makes it harder to stop gaining.
Can Hormonal Resistance Be Improved?
Yes. The goal is to improve insulin sensitivity first, which often helps leptin signaling as well. Want to know about helpful strategies and not sure where to begin? Let’s talk it’s free.
Small metabolic improvements can significantly shift hormonal balance over time. Final Thoughts Obesity is not just a matter of overeating. It is often the result of disrupted hormonal communication. While both insulin and leptin play powerful roles, insulin resistance usually initiates the process, and leptin resistance reinforces it. Understanding this hormonal connection changes how we approach weight management shifting the focus from willpower to metabolic health. When hormones are balanced, weight regulation becomes much easier.