Decision Making & Problem Solving Management in MIS & DSS
510 likes | 529 Vues
This chapter explores Information Systems, Decision Support Systems, Group Decision Support Systems, and Artificial Intelligence in decision-making processes. Learn about optimization, heuristic approaches, MIS, DSS, and key terms in problem-solving stages. Discover the role of reports in MIS, Decision Support Systems like What-if analysis and Goal-seeking, Group Decision Support Systems, and AI technologies such as genetic algorithms, expert systems, and robotics. Explore how AI systems simulate human behavior and learn about specialized systems like virtual reality, geographic information systems, and game theory.

Decision Making & Problem Solving Management in MIS & DSS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Please discontinue use of cell phone and turn off ringer Chapter 9 Information, Decision Support… Decision Making and Problem Solving Management Information Systems Decision Support Systems Group Decision Support Systems Artificial Intelligence and Special-Purpose Systems
Decision Making Problem Solving Decision Making & Problem Solving Process Intelligence Stage Potential Problems and opportunities are identified and defined Design Stage Alternative solutions to the problem are developed Choice Stage Select a course of action Implementation Solution put into effect Monitoring Evaluate the implementation
MIS vs. DSS • A MIS sheds light on a wide-range of common, day-to-day business decisions. • A DSS supports decision making for specific unique and difficult decisions.
Optimization and Heuristic Approaches • An optimization model finds the best solution, usually the one that will best help individuals or organizations meet their goals. • Heuristics, “rules of thumb”—commonly accepted guidelines or procedures that usually find a good solution, but not necessarily the optimal.
Key Terms • Management Information System (MIS) • Scheduled report • Demand report • Exception report 9.2 Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS) • MIS: an information system designed to provide routine information to managers and decision makers
Reports, Reports, Reports www.cognos.com/products/business_intelligence/reporting_sapbw/
Reports • Scheduled Reports are produced periodically on a schedule; daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, annualy, ect. • Demand Reports are developed to get certain information at a person’s request. • Exception Reports are automatically produced when a situation is unusual or requires action.
Key Terms • Decision Support System • What-if analysis • Goal-seeking analysis 9.3 Decision Support Systems
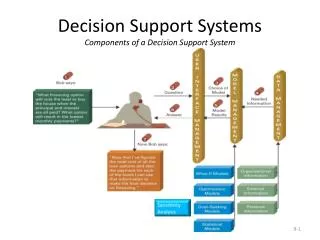
Decision Support Systems • A decision support system (DSS) is an information system used to support problem-specific decision making. www.epocrates.com
What-if? • What-if analysis is the process of making hypothetical changes to problem data and observing the impact on the results. What-if is used in projecting paths of hurricanes
Goal-seeking • Goal-seeking analysis is the process of determining what problem data is required for a given result. What must be done in order to safely withdraw troops within a year?
Key Terms • Group decision support system (GDSS) • Groupware 9.4 Group Decision Support Systems
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) • A GDSS or computerized collaborative work system is designed to provide effective support in group decision-making settings. A GDSS is flexible, supports anonymous input, and reduces negative group dynamics
Groupware • GDSS software, called groupware, helps with joint work group scheduling, communication, and management. www.lotus.com
9.5 AI and Special-Purpose Systems Key Terms • Genetic algorithm • Intelligent agent • Expert system (ES) • Virtual reality • Geographic information system (GIS) • Game theory • Robotics • Vision systems • Natural language processing • Learning systems • Neural network • Fuzzy logic
An Overview of AI • AI systems simulate human thought and behavior. www.cyc.com
Robotics • Robotics involves developing mechanical or computer devices to perform tasks that require a high degree of precision or are tedious or hazardous for humans.
Other Forms of AI • Vision systems permit computers to capture store and interpret visual imaged and pictures. • Natural language processing, or speech recognition, allows a computer to understand and react to statements and commands made in a natural language. • Learning systems allow the computer to change how it functions or reacts to situations based on feedback it receives.
Other Forms of AI • A neural network is a computer system that can act like or simulate the functioning of the human brain. • Fuzzy logic allows computers to deal with ambiguous criteria or probabilities and events that are not mutually exclusive. • A genetic algorithm is an approach to solving large, complex problems where a number of algorithms or models change and evolve until the best one emerges.
Other Forms of AI • An intelligent agent consists of programs and a knowledge base used to perform a specific task for a person, a process, or another program. • As expert system (ES) acts or behaves like a human expert in a field or area. Physicians rely on expert systems to analyze complex medical data.
Specialized Systems • Virtual reality is a computer-simulated environment or event.
Specialized Systems • A geographic information system (GIS) is capable of storing, manipulating, and displaying geographic or spatial information including maps of locations or regions around the world.
Specialized Systems • Game theory involves developing strategies for people, organizations, or even countries that are competing against each other. • Informatics combines traditional disciplines, like science and medicine, with computer systems and technology.
Don’t forget to turn your phone on!! Chapter 9 Questions?
Systems Development An Overview of Systems Development Tools and Techniques for Systems Development Systems Investigation Systems Design Systems Implementation Systems Maintenance and Review Please discontinue use of cell phone and turn off ringer Chapter 10
10.1 An Overview of Systems Development Key Terms • Systems development • Systems development life cycle • System stakeholders • Systems analyst • End-user systems development
Systems Development www.aim.fsu.edu Systems development is the activity of creating new or modifying existing information systems. The systems development life cycle (SDLC) is the ongoing activities associated with the system development process including investigation, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance and review.
Systems Analyst Systems Analyst: professional who specializes in analyzing and designing systems. Knowledge Workers programmers Stakeholders are those that stand to benefit from a new system.
End-User Development Non-tech users are becoming increasingly involved in system and software development in businesses and organizations. Why? They understand the problems at hand They are increasingly technically savvy Software development tools are increasingly easier to use Programmers are not able to keep up with organization demands
10.2 Tools and Techniques for Systems Development Key Terms • Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools • Flowchart • Decision Table • Project management • Prototyping • Outsourcing • Object-oriented systems development
CASE Tools Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools automate many of the tasks required in a systems development effort
Flowchart A flowchartis a system design diagram that charts the path from a starting point to the final goal of a system. A decision table is a systems development tool that displays the various conditions that could exist in a system and the different actions that the computer should take as a result of these conditions.
Project Management Gantt Chart The overall purpose of project management is to plan, monitor, and control necessary development activities.
Iterative Approach With the iterative approach, each phase of the SDLC is repeated several times (iterated). Prototypingtypically involves creating a preliminary model or version of a major subsystem, or a small or scaled-down version of the entire system.
Outsourcing and Offshoring Outsourcingis a business’ use of an outside company to take over portions of its workload. Offshoring relocates an entire production line to another location, typically in another country with cheaper labor, lower taxes, or other financial benefits.
10.3 Systems Investigation Key Terms • Systems investigation • Feasibility analysis SDLC
Systems Investigation • The overall purpose of systems investigationis to determine whether or not the objectives met by the existing system are satisfying the goals of the organization. • A key part of the systems investigation phase is feasibility analysis, which investigates the problem to be solved or opportunity to be met.
10.4 Systems Analysis Key Terms • Systems analysis • Requirements analysis SDLC
Systems Analysis Systems analysis attempts to understand how the existing system helps solve the problem identified in systems investigation and answers the question, “What must the computer system do to solve the problem?” The overall purpose of requirements analysisis to determine user, stakeholder, and organizational needs.
10.5 Systems Design Key Terms • Systems design • Request for proposal (RFP) SDLC
Systems Design The purpose of systems design is to select and plan a system that meets therequirements defined in the requirements analysis. The request for proposal (RFP) is generated during systems development when an organization wants a computer systems vendor to submit a bid for a new or modified system.
10.6Systems Implementation Key Terms • Systems implementation • Direct conversion • Phase-in approach • Pilot startup • User acceptance document SDLC
Systems Implementation Systems implementation includes hardware acquisition, software acquisition or development, user preparation, hiring and training of personnel, site and data preparation, installation, testing, startup, and user acceptance.
10.7 Systems Maintenance and Review Key Terms • Systems maintenance • Systems review SDLC
Systems Maintenance and Review Systems maintenance involves checking, changing, and enhancing the system to make it more useful in achieving user and organizational goals. Systems review, the final phase of the systemsdevelopment life cycle, is the process of analyzing systems to make sure that they are operating as intended.