IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS
190 likes | 432 Vues
IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS. Methanol (wood alcohol): CH 3 OH Production: Useful as a solvent and industrial starting material Highly toxic, if taken internally causes blindness and/or death. IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS (continued). Ethanol (ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol): CH 3 CH 2 OH

IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
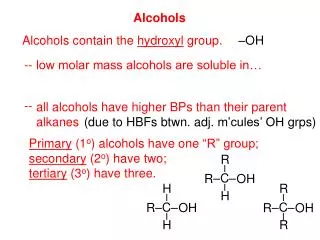
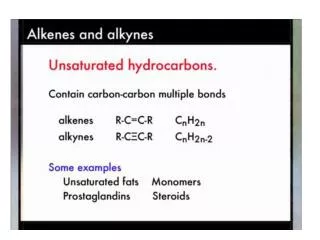
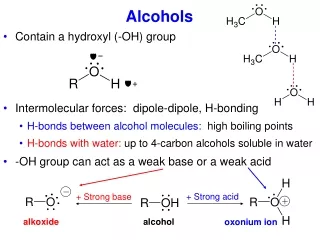
IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS • Methanol (wood alcohol): CH3OH • Production: • Useful as a solvent and industrial starting material • Highly toxic, if taken internally causes blindness and/or death
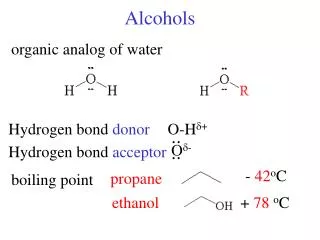
IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS (continued) • Ethanol (ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol): CH3CH2OH • Produced commercially from ethylene and through biological (yeast) fermentation of carbohydrates • Useful as a solvent, industrial starting material, fuel (gasohol), and found in alcoholic beverages • Moderately toxic
ETHANOL PRODUCTION METHODS • Hydration of ethylene: • Yeast fermentation of carbohydrates:
IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS (continued) • 2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol) is the main component of rubbing alcohol. • 1,2,3-Propanetriol (glycerol) is used as a food moistening agent (nontoxic) and for its soothing qualities (soaps).
IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS (continued) • Antifreezes1,2-ethanediol (ethylene glycol) • 1,2-propanediol (propylene glycol)
PHENOLS • Phenol behaves as a weak acid in water. • Phenol can react with bases to form salt.
USES OF PHENOLS • In a dilute solution, phenol is used as a disinfectant. • Phenol derivatives used as disinfectants:
USES OF PHENOLS (continued) • Phenol derivatives used as antioxidants in food:
NAMING ETHERS • IUPAC name: Name the smaller of the two R groups as an alkoxy group attached to the parent chain by replacing the –yl ending of the R group with –oxy. • Common name: Name the groups attached to the oxygen alphabetically and add the word ether. common: sec-butyl ethyl ether
CYCLIC ETHERS • Heterocyclic rings contain atoms other than carbon in the ring.
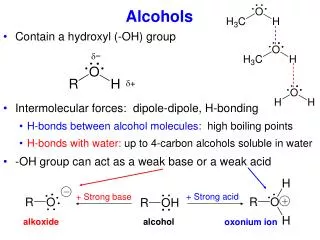
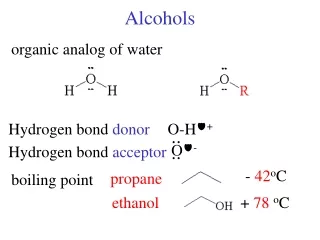
PROPERTIES OF ETHERS • Much less polar than alcohols • More soluble in water than alkanes, but less soluble than alcohols • Low boiling and melting points because of the inability to hydrogen bond between molecules • Inert and do not react with most reagents (like alkanes) • Highly flammable (like alkanes)
PROPERTIES OF ETHERS (continued) • Hydrogen bonding of dimethyl ether: (a) with water and (b) no hydrogen bonding in the pure state.
THIOLS: THE –SH (SULFHYDRYL) GROUP • Most distinguishing characteristic is their strong and offensive odor • ethanethiol – added to natural gas • 1-propanethiol – odor in garlic and onions • trans-2-butene-1-thiol – odor associated with skunks
THIOL REACTIONS • Oxidation forms disulfide (-S-S-) linkages, which are important structural features of some proteins: • Specific example:
THIOL REACTIONS (continued) • Oxidation reactions can be reversed with a reducing agent (H):
THIOL REACTIONS (continued) • Reacts with heavy metals (Pb2+, Hg2+) to form insoluble compounds, with adverse biological results:
POLYFUNCTIONAL COMPOUNDS • Polyfunctional compounds are compounds with two or more functional groups. • Functional groups determine chemical properties of compounds. • Example: