Analyzing Power System Faults: Sequence Component Theory and Trip Schemes
40 likes | 172 Vues
This document explores the complex nature of power system faults through the lens of sequence component theory. It details the calculations for positive, negative, and zero sequence components, offering insights into the fault analysis process. Additionally, it addresses communication issues related to trip schemes, including false tripping incidents, and outlines the steps needed to effectively design a robust fault detection and management system. This analysis is crucial for improving the reliability and safety of electrical systems.

Analyzing Power System Faults: Sequence Component Theory and Trip Schemes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
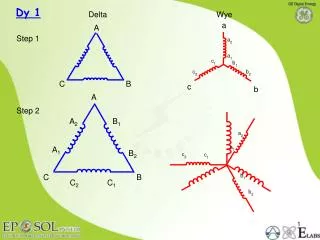
c b A a2 A2 B1 a2 a1 c2 c1 c1 a1 b1 c2 b2 b1 A1 B2 b2 C B C2 C1 Dy 1 Delta Wye a A Step 1 C B Step 2
A A2 B1 A1 B2 C2 C1 Step 3 C B Step 4 D / Y A2 A1 a1 a2 a A b1 b2 B2 B1 b B C2 c2 C1 c1 c C
POWER SYSTEM FAULTS SEQUENCE COMPONENT THEORY: Ib2 Ib2 Ib0 Ia1 Ia1 Ib1 Ib1 Ib1 Ic1 Ic1 Ic2 Ic2 Ia2 Ia2 Ib= Ib0 + Ib1 + Ib2 Ib2 +ve Sequence Comps Ia= Ia0 + Ia1 + Ia2 Ic= Ic0 + Ic1 + Ic2 Ia0 -ve Sequence Comps Ic0 Ic2 Ia2 Ic1 Ia1 Ib0 Ib0 Ia0 Ia0 Ia=4.7133 +2.955 +9.258 Ia= 5 Ib=4.7133 +2.955 +9.258 Ib= 10 Ic=4.7133 +2.955 +9.258 Ic= 15 Ic0 Ic0 Zero Sequence Comps
Direct Transfer Trip Scheme - ISSUES Communication Error False Tripping A B