Odana Hills Golf Course Distance Analysis for Precision Golfing
250 likes | 344 Vues
This project at Odana Hills Golf Course in Madison, WI utilized GPS data collection to measure and analyze distances for tee, fairway, and green locations. The objective was to compare measured distances to those posted at the course to ensure accuracy.

Odana Hills Golf Course Distance Analysis for Precision Golfing
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Golf Course Distance Analysis Brad Herried Jordan Gonnering
Introduction “Golf is not, on the whole, a game for realists. By its exactitudes of measurement it invites the attention of perfectionists” -Heywood Hale Broun, American Sportswriter
Objectives • Repeatedly measure (for accuracy) location of tee, middle of fairway, and green • Calculate distances of holes using latitude and longitude of measurements • Compare measured distances to those posted at course
Site Selection • Odana Hills Golf Course, Madison, WI • Par 72, 6572 yards from Blue Tees • One of four City of Madison owned golf courses
Data Sources/Software • GPS data: collected with Garmin receivers • Satellite Image: WisconsinView download portal • Road Layers: USGS Tiger files • Data acquired into ArcMap using Minnesota DNR’s shapefile creator
Methods • Using two GPS handheld receivers, measurements were taken in 1 minute intervals at each hole • 15 measurements at tee • 40 measurements at fairway (200 yd marker) • 15 measurements at green • Data was collected at holes 1, 2, and 7 (par 4, par 5, par 3)
Example A A B B 15 readings 20 readings 15 readings
Data Analysis - Overview • After these positions were recorded into the GPS as waypoints, they needed to be averaged to find the most accurate point • Data was downloaded into ArcMap and statistical analysis was completed to find standard deviation and average for (x,y,z)
Data Analysis - Overview • With these averages computed, an (x,y,z) coordinate is available to compute distances for each of our tee, fairway, and green locations • Using the distance formula, calculated distances for each hole • (tee to fairway) + (fairway to green) = hole distance • Compared these distances to what the golf course provides
Data comparison • After finding the mean easting and northing coordinates, standard deviation and variance were calculated to best describe accuracy
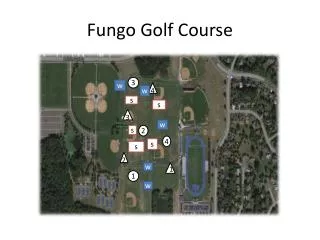
Spatial Representation • To best accompany our results and comparisons, maps show our spatial accuracy • Maps display holes 1, 2, 7 and zoom into areas for best viewing of data • Notice scale bar and accuracy standards
Discussion • Accuracy was maximized by using multiple readings and multiple receivers • Distances were within ten yards, but when considering standard deviation, results were not as accurate as hoped • By comparing this to ground truth (yardage measurements by course), we found a fairly accurate hole measure
Points to consider • Possibility to measure more holes • Time constraint? Golf course availability? • Taking more measurements leads to better accuracy (over time) • Distances measured on ground or through the air? Which is more vital to golfers? • New advances in golf cart GPS makes this sort of testing obsolete