Genetic Toxicology 의과대학 미생물학교실
170 likes | 736 Vues
Genetic Toxicology 의과대학 미생물학교실. Genetic toxicology Subspeciality of toxicology Involves the identification and analysis of agents with toxicity directed to the hereditary components of living organisms. Background

Genetic Toxicology 의과대학 미생물학교실
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Genetic Toxicology 의과대학 미생물학교실
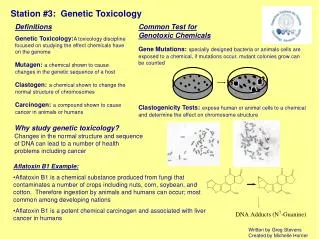
Genetic toxicology • Subspeciality of toxicology • Involves the identification and analysis of agents with toxicity directed to the hereditary components of living organisms. • Background • Agents that induces alterations in nucleic acids and associated components at subtoxic exposure levels, resulting in modified hereditary characteristics or DNA inactivation, are classified as genotoxic. • ※DNA repair system 1) Excision repair ① Base excision repair ② Nucleotide excision repair 2) Recombinational repair 3) SOS repair ⇒ Bacteria에서 가장 많이 연구되어 있는 system
1) Excision repair Nucleotide excision repair :The mechanism of excision repair of pyrimidine photodimers
1) Excision repair Base excision repair: DNA glycosylase hydrolyze the glycosidic bonds of their corresponding altered base
2) Recombinational repair: In recombination repair, the gap in a newly synthesized DNA strand opposite a damage site is filled by the corresponding segment from its sister duplex
자연계에서 가장 강한 mutagen은 UV light이다. UV에 의해 손상된 DNA는 excision repair와 recombinational repair에 의해 다시 정확하게 원상복구가 되는데 이는 두 repair system은 DNA template를 기본으로 하여 repair되기 때문이며 DNA template를 기본으로 repair할 수 없을 정도로 DNA 손상이 생기면 세포는 생존을 위해 mutagenesis를 일으키는 repair system인 SOS repair system을 작동시키게 된다. ⇒ SOS system에서 DNA recovery는 DNA template 없이 진행되므로 많은 실수를 일으키게 되며 따라서 결과적으로 더 많은 돌연변이를 유발하게 된다. ⇒ SOS system에 관여하는 유전자: uvrA, uvrB, uvrD, recA, lexA, ssb, ruv, recN, umuC, umuD
Model for the SOS regulatory system ⇐ SOS 반응의 기작. DNA 손상이 일어나면 RecA 단백질을 단백질 분해효소로 전환시켜서 LexA 단백질을 절단한다. LexA 단백질은 정상적으로 recA 유전자와 DNA 수복 유전자인 uvrA와 uvrB의 활성을 억제한다. LexA가 불활성화되면 이들 유전자가 활성화된다.
2. Genotoxic substances usually have common chemical or physical properties faciliating their interaction with nucleic acids. 3. Mutagens compose a subset of geneotoxics, demonstrated experimentally to induce specific classes of stable changes in, 1) the nucleotide sequence of genes 2) chromosome structure 3) chromosome number
Materials & Method • Substrate method • beta-galactosidase; alkaline phosphatase (AP) • ONPG (o-Nitrophenyl-b-D galactoside) • ; beta-galactopyranoside • ⇒ beta-gal substrate • 4-Nitroquinaline N-oxide; Mutagen • PQ37 strain
PQ37 strain • Deletion of the normal lac region • The strain is made genetically more susceptible to • genotoxic agents: uvrA mutation • Constitutive synthesis of alkaline phosphatase: • independent of SOS control UmuC, UmuD: misincorporated base의 chain elongation
Method: standard procedure for the SOS chromotest 1. Culture PQ37 strain(3ml) at 37℃ for 18 h 2. 1/10 dilution culture at 37℃ for 2 h (100 ㎕ culture medium을 900 ㎕ fresh medium으로 희석; 약 2×108 bacteria/ml) 3. Add 0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 ㎍ mutagen(4-Nitroquinoline N-oxide)/배양액(ml), respectively 4. Shaking Incubation at 37℃ for 1 h 5. 1/10 dilution culture at 37℃ for 1 or 2 h ; bacteria growth (1 ml의 culture medium을 9 ml fresh medium으로 희석) 6. 배양액 0.2 ml을 β-galactosidase측정하기 위해 각 tube에 분주 0 1 2 3 1) Add Strain(0.2 ml) (×1) 2) Add B buffer(1.8 ml) (×9) 3) 0.1% SDS (50㎕) 4) voltex short time 5) 37℃에서 15~20분간 반응 6) Add ONPG sol.(0.4 ml) (×2) 7) Incubation at R.T for 30~90min 8) Reaction time(t = ) 9) Add 1M Na2CO3 (1 ml) 10) A420nm측정
LB medium (Luria-Bertani Medium) per liter, Distilled water Bacto-tryptone 10g Bacto-yeast extract 5g NaCl 10g B buffer Na2HPO4 16.1g NaH2PO4 7H2O 5.5g KCl 0.75g Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) 1g b-mercaptoethanol 2.7ml OPNG solution (4mg/ml) o-nitrophenyl-b-D-galactopyranoside 400mg 0.1M Na2HPO4 ·7H2O 61ml 0.1M NaH2PO4·H2O 39ml
Conclusion SOS 조절계에서, DNA 손상이 세포에 조난신호를 보내면 DNA 수복에 관련된 많은 수의 세포성 기능이 지속적으로 활성화된다. SOS system은 정상적으로 LexA 단백질에 의해 억제되나, DNA 손상의 결과로 활성화된 단백질 분해효소인 RecA 는 LexA를 불활성화 시킨다. SOS system의 DNA 수선기작은 유전자 주형을 기본으로 하지 않으므로 선천적으로 잘못되기 쉬우며 따라서 많은 돌연변이가 발생한다. 이러한 이유로 SOS regulatory system은 화학약품이나 방사선 같은 여러 매체에 의한 DNA 손상 및 돌연변이 형성 실험에 적용되고 있다.