Understanding Plant Reproduction: Germination, Fertilization, and Growth Processes
260 likes | 385 Vues
Discover the fascinating processes of plant reproduction, including germination, fertilization, and the development of seeds into mature plants. Learn about the roles of various plant parts such as stamen, pistil, leaves, roots, and stems in reproduction. Explore annual, biennial, and perennial plant lifespans, and the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. This guide elucidates how seeds germinate under favorable conditions and how various methods like stem cuttings and tubers contribute to plant propagation.

Understanding Plant Reproduction: Germination, Fertilization, and Growth Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
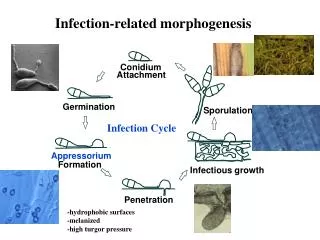
Germination The stage when seeds scatter from the parent plant and either lie on the ground and become dormant or grow immediately given the right conditions. The roots begin to grow downward, while the leave and stem grow upward.
stamen Male part of the flower that has an anther on a stalk.
Fertilization When pollen enters the ovule
perennial The plants whose life span last more than two years.
Pistil The female part of the flower that holds the flowers ovary, the style, and stigma.
Seed The ovule that contains the fertilized egg. A seed is formed from the ovary which often protects the seed.
Plant Development Over time the seed grows into a mature plant with the structures necessary to produce more plants.
Biennial Plants who complete their lifespan in two years.
Annual Flowers that complete their lifespan in one growing season.
Sexual Reproduction Process that requires 2 parents who combine their genetic material to produce a new organism that is different than the parents.
Asexual Reproduction Process of reproduction that involves only one parent and produces offspring that is identical to the parent.
Runners Stems that run along the ground.
Bulbs Big buds made of a stem and special types of leaves.
What happens after the ovule is fertilized? Once the ovule is fertilized it develops into a seed.
What is the main function of the flower petals? To attract polinators
Which part of the plant uses the sun’s energy to make food? Leaves
Which plant structures take in water and minerals used by the plant? Xylem
What are the conditions needed for a seed to germinate? Water and warmth
What is the purpose of a fruit? To protect the seed.
What happens to roots, leaves, and stems during germination? Stems and leaves grow upward and roots grow down.
Explain how stem cuttings develop into a new plant? When piece of cut stem is planted, roots may form from the cutting, and then the full plant develops.
How can a sweet potato produce new plants? The eyes or buds grow into roots and shoots to produce a new plant.
How can African violets produce new plants? They produce plants from leaves place on top of the soil.
What do bulbs and tubers have in common? All of these have underground stems.
What part of a tuber grows into roots and shoots to produce new plants? The eyes or buds