Dialog Boxes
160 likes | 402 Vues
Dialog Boxes. Cooper 30. Topics. Introduction Dialog Box Basics Modal Dialog Boxes Modeless Dialog Boxes Modeless Dialog Confusion Solutions. Topics. Property Dialogs Function Dialogs Bulletin Dialogs Process Dialogs Bulletin Dialog Boxes. Introduction.

Dialog Boxes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dialog Boxes Cooper 30 William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Topics • Introduction • Dialog Box Basics • Modal Dialog Boxes • Modeless Dialog Boxes • Modeless DialogConfusion Solutions William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Topics • Property Dialogs • Function Dialogs • Bulletin Dialogs • Process Dialogs • Bulletin Dialog Boxes William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Introduction • Secondary, not primary interaction • Suspends normal processing • Breaks the UI flow • Superimposed over current screen • Used for infrequent functions • Encapsulates and groups functions William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Dialog Box Basics • Must be • Speedy • Smooth • Compact • Powerful • Clear • Self-explanatory William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Dialog Box Basics • Called and controlled by owner (parent) • Contain controls • May/may not have title or caption • Two terminating buttons – OK, Cancel • No standard layout William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
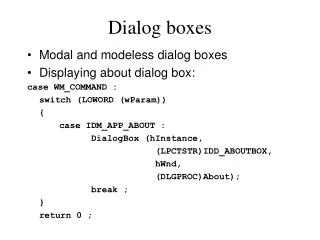
Modal Dialog Boxes • Most common dialog box • Suspends program execution • Disables other program controls • Must close to continue program • Application modal • System modal William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Modeless Dialog Boxes • Less common than modal dialogs • Program and controls still active • Few behavioral conventions • Can be confusing since unexpected • Underlying assumptions can change William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Modeless DialogConfusion Solutions • Evolutionary Solution • Visually differentiate modeless and modal dialogs • Consistent button terminology • Do not change captions when selections are made William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Modeless DialogConfusion Solutions • Radical solution • Eliminate modeless dialogs • Implement as toolbars instead • Floating • Docked William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Property Dialogs • Usually modal • Specific group of functionalities • Tied to an object • Object-verb form William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Function Dialogs • Usually modal • Single function • Printing • Spell checking • Inserting objects into documents • Launch and configure an action William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Bulletin Dialogs • Messages to user • Modal • Issued by the system William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Process Dialogs • Created by the application • Indicate program is busy and “stupid” • Four tasks • Indicate program is busy with a time consuming process • Indicate normality • Indicate remaining time • Allow user to cancel without penalty William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Bulletin Dialog Boxes • Reports problems • Usually contains text, graphic and OK button • Most abused element of GUI • Should never be transitory William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu
Questions & Discussion William H. Bowers – whb108@psu.edu