Action 1: Mission/task analysis
30 likes | 438 Vues
Action 2: Assess hazard severity. Action 4: Complete assessment. Action 3: Assess mishap probability. Mishap Probability. Frequen t. Occasional. Seldom. Unlikely. Likely. Action 2: Establish accountability. Action 3: Provide support. Action 1: Make implemen- tation clear. A.

Action 1: Mission/task analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
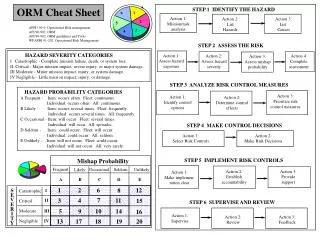
Action 2: Assess hazard severity Action 4: Complete assessment Action 3: Assess mishap probability Mishap Probability Frequent Occasional Seldom Unlikely Likely Action 2: Establish accountability Action 3: Provide support Action 1: Make implemen- tation clear A B C D E 1 2 6 12 8 S I Catastrophic E 7 3 4 11 15 V II Critical E 10 14 9 16 R 5 Moderate III I Action 1: Supervise Action 2: Review Action 3: Feedback 17 18 19 20 T 13 Negligible IV Y ORM Cheat Sheet STEP 1 IDENTIFY THE HAZARD 1 6 Action 1: Mission/task analysis Action 2: List Hazards Action 3: List Causes 2 5 AFPD 90-9, Operational Risk management AFI 90-901, ORM AFI 90-902, ORM guidelines and Tools WPAFBI 91-202, Operational Risk Management 3 4 STEP 2 ASSESS THE RISK HAZARD SEVERITY CATEGORIES I Catastrophic - Complete mission failure, death, or system loss. II Critical - Major mission impact, severe injury, or major system damage. III Moderate - Minor mission impact, injury, or system damage. IV Negligible - Little mission impact, injury, or damage. Action 1: Assess hazard exposure STEP 3 ANALYZE RISK CONTROL MEASURES HAZARD PROBABILITY CATEGORIES A Frequent - Item: occurs often. Fleet: continuous. Individual: occurs often. All: continuous. B Likely - Item: occurs several times. Fleet: frequently. Individual: occurs several times. All: frequently. C Occasional - Item: will occur. Fleet: several times. Individual: will occu. All: sporadic. D Seldom - Item: could occur. Fleet: will occur. Individual: could occur. All: seldom. E Unlikely - Item: will not occur. Fleet: could occur. Individual: will not occur. All: very rarely. Action 3: Prioritize risk control measures Action 1: Identify control options Action 2: Determine control effects STEP 4 MAKE CONTROL DECISIONS Action 1: Select Risk Controls Action 2: Make Risk Decisions STEP 5 IMPLEMENT RISK CONTROLS STEP 6 SUPERVISE AND REVIEW
ORM Cheat Sheet The 5 M Model Management Man Machine Mission Media RISK CONTROL OPTIONS MATRIX Engineer Guard Improve Task Design Limit Exposure Selection of Personnel Train and Educate Warn Motivate Reduce Effects Rehabilitate MACRO CONTROL OPTIONS LIST Reject Avoid Delay Transfer Spread Compensate Reduce ORDER OF PRECEDENCE 1. Design for Minimum Risk 2. Incorporate Safety Devices 3. Provide Warning Devices 4. Procedures & Training THE INVOLVEMENT CONTINUUM User Ownership Co-ownership STRONGER Team Member Input Coordination Comment And Feedback Robot WEAKER THE POWER OF COMMAND Sustained consistent behavior STRONGER On-going personal behavior Accountability actions and follow up Follow up inquiries by phone and visits Verbal support in staff meetings Sign directives WEAKER 7 PRIMARY HAZARD IDENTIFICATION TOOLS Operations Analysis - a block diagram, flow chart, or timeline that describes the operation. Preliminary Hazard Analysis - an examination for sources of hazards, usually related to energy. What If Analysis - a group brainstorming technique. “What if this happens?” Scenario Process - stories describing conceivable mishaps and consequences. Logic Diagrams - “tree” shaped diagrams examining hazards in detail: positive, negative, and risk event diagrams. Change Analysis - compares changes to a baseline to determine significance. Cause and Effect Diagrams - fishbone diagram to examine many causes of a mishap. • HAZARDS ARE CAUSED • BY ENERGY • Force Acceleration • Chemical Vibration • Electrical Environmental • Kinetic Pressure • Potential Thermal • Radiation Humans