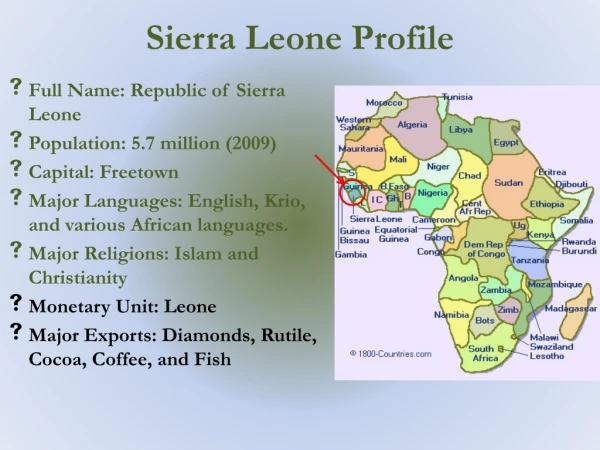
Sierra Leone
180 likes | 414 Vues
Sierra Leone. A brief look at geo-political changes - 2006. Order of Talk. Changes in US Foreign Policy Changes in UK Foreign Policy The rising stars – China, India, BRIC countries What are the apparent geo-political priorities? The EU and its expansion

Sierra Leone
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sierra Leone A brief look at geo-political changes - 2006
Order of Talk • Changes in US Foreign Policy • Changes in UK Foreign Policy • The rising stars – China, India, BRIC countries • What are the apparent geo-political priorities? • The EU and its expansion • Globalisation and Free Trade – some thoughts • Questions and Answers
The changes in US foreign Policy -1 • 15 new positions created at US Embassy in China • 12 new position at US Embassy in India • 5 at US Embassy in Jakarta • Overall 74 new posts, of which over three quarters were in developing economies • Going to fund these are 61 positions of which 10 are in Russia, 7 in Germany, 2 0r 3 in Belgium, Poland, Italy, Spain, Japan and perhaps surprisingly Brazil • BRIC countries?
Changes in US foreign policy - 2 • In his recent trip to Asia President Bush called at Afghanistan – reassurance. • Then India, the fast rising economic powerhouse and seen by ‘west’ as counterbalance to China. • Then Pakistan, like India a nuclear power and whose volatile regions provide cover of al-Qaida training and possibly Bin Laden
US Foreign Policy - 3 • US changing its focus. US diplomats have been killed in Karachi etc and attempts elsewhere • Reaction to spread/influence of Islamic fundamentalism. • These changes are also posing threats to Europe and so policies are changing • The role of NATO and EU in ‘European’ defence?
UK Foreign Policy Changes - 1 • ‘the world is more complex and circumstances are changing’ Michael Jay, Head of FO – March 2006. • Shifting resources from Europe to Asia • 153 Embassies and high commissions + 10 missions to UN etc and 70 Consulates • Priorities – counter-terrorism, combating illegal immigration, drug-trafficking and other international crime, conflict resolution
UK Foreign Policy Changes - 2 • Continued – maintain interests in Europe, sustainable development and UK security • Closing 9 Embassies and High Commissions, Vanuatu, Tonga, Kiribati, Lesotho, Swaziland and Madagascar. • New establishments include: Baghdad, Kabul and North Korea and recruitment has concentrated on counter-terrorism and drug-trafficking • Embassy protection costs have doubled to £4.8m in 2004-05.
Other EU States – changes in foreign policy • Germany – post re-unification – 35 new embassies and consulates. New presence in North Africa (energy), Middle East (energy) and countries such as Indonesia, Pakistan and Afghanistan. Engaging with Islam (large population in Germany and Mrs. Merkle has said nothing on Turkish Accession to EU – 2015? • France – already has large presence in Middle East (history), increased security and staff working on terrorism and may share some facilities with Germany • What of EU diplomatic missions and Constitution has role for EU Foreign Minister and seat on Permanent Members of Security Council
Is it all west to east? • China – busy in Africa, Latin America and Far East. Needs ALL major industrial imports, especially energy. • Maintains an embassy in almost every country in the world and has 5000+ officials working overseas.
What are the priorities? • How does China view the world? Look at its 61 Consular Offices and see where they are located – largest number in US, then Japan and they don’t always seem too close, Britain, Germany, France, Australia, Canada and South Africa. They spend a lot in Pakistan, which might be seen to counterbalance of US/India relations (new £44m port at Gwadar, Angola which has just received a billion dollar credit line to purchase Chinese goods
The world through three different sets of eyes • Washington • FIRST RANK MISSIONS -Beijing as the most important long-term military and economic threat to US global influence. Watches Japan closely as it is industrial power and like China buys US debt. Also Berlin, London and Paris • SECOND RANK – UN, India (nuclear power and counterbalance to Islamabad), Ottawa – close neighbour and important for trade (NAFTA), Brussels, Moscow, Tel Aviv, Rome, Seoul (growing in importance), Mexico City again NAFTA and security of southern borders, Islamabad. • THIRD RANK – Brasilia which is the dominant South American power and a BRIC country. May be a potential nuclear power. Cairo, friendly Arab power and gateway to canal and Red Sea, Amman which is another friend in Middle East, Riyadh and oil + military bases, Abu Dhabi which is set to be larger energy exporter to US and EU
World through different sets of eyes - 2 Washington continued • FOURTH RANK Bangkok, Bahrain, Pretoria • London FIRST RANK– US, UN, Brussels, Paris SECOND RANK– Rome, Berlin, Beijing, Moscow, Delhi • THIRD RANK – Riyadh, Baghdad, Cairo, Pretoria • Fourth rank – Tel Aviv, Ottawa, Canberra
World through different eyes • Beijing • FIRST RANK – US, Tokyo • SECOND RANK – London, Berlin, Islamabad, North Korea, Moscow, South Korea, Paris, Rome • THIRD RANK – Riyadh, Tehran, Pretoria, New Delhi, Ottawa, Canberra, Argentina • FOURTH RANK – Angola, Zimbabwe (raw materials), Chile, Cambodia, Vietnam,
Expansion of EU • Treaty of Rome 1957 – now 25, soon 27. • Europe united, Single market, Single Currency. • Regional Policy – 75% • Budget – 1.1% of Net National Income of member states • Influence • Major Aid contributor • Could go to 30+ - Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Turkey and has special relations with Russia, parts of North Africa and Middle East
Globalisation - 1 • ‘everyone will gain’ • ‘Free trade greater liberator that aid’ • Outsource, low wage to high income • Low value goods made in developing countries, high value in developed • Boost demand in developing economies and it will boost business in developed world • Speed of change, internet, high intellect research and high end development going to Budapest, South Africa and India • Stagnated wage rates in US, what will happen to middle grade workers in London, Paris etc? • Educated global elite who can move easily around business centres? • Look at some of the reasons why the French and Dutch rejected proposed EU Constitution
Globalisation - 2 • Where will Africa fit into this? Look at its recent history • How will Sierra Leone have to change to meet this fast changing, information driven age? • What should be priorities of Sierra Leone? • I can give you sites to visit to develop your interest in global issues. • Thanks, John