X-ray Diffraction & Crystal Structure Basic Concepts
930 likes | 1.63k Vues
X-ray Diffraction & Crystal Structure Basic Concepts. T. P. Radhakrishnan School of Chemistry, University of Hyderabad Email: tprsc@uohyd.ernet.in Web: http://chemistry.uohyd.ernet.in/~tpr/. This powerpoint presentation is available at the following website.

X-ray Diffraction & Crystal Structure Basic Concepts
E N D
Presentation Transcript
X-ray Diffraction & Crystal Structure Basic Concepts T. P. Radhakrishnan School of Chemistry, University of Hyderabad Email: tprsc@uohyd.ernet.in Web: http://chemistry.uohyd.ernet.in/~tpr/
This powerpoint presentation is available at the following website http://chemistry.uohyd.ernet.in/~ch521/ Click on x-ray_powd.ppt
Outline • Crystals • symmetry • classification of lattices • Miller planes • Waves • phase, amplitude • superposition of waves • Bragg law • Powder diffraction • Systematic absences, Structure factor • Single crystals - Solution and Refinement • Diffraction line width • Applications of Powder diffraction
Crystals • Waves • Bragg Law • Powder diffraction • Systematic absences, Structure factor • Single crystals - Solution and Refinement • Diffraction line width • Applications of powder diffraction
Molecular Structure Optical spectroscopy – IR, UV-Vis Magnetic resonance – NMR, ESR Mass spectrometry X-ray diffraction High resolution microscopy
A B 5 Å 5 Å C D 20 Å 5 Å Molecular Structure Resolved by Atomic Force Microscopy Pentacene on Cu(111) B. STM image C, D. AFM images (tip modified with CO molecule) A. Molecular model of pentacene Gross, Mohn, Moll, Liljeroth, Meyer, Science 2009, 325, 1110
Crystal and its structure 3-dimensions Anthony, Raghavaiah, Radhakrishnan, Cryst. Growth Des. 2003, 3, 631
STM image of 1,3-diheptadecylisophthalate on HOPG (with a model of two molecules) Plass, Kim, Matzger, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9042
Point group symmetries : Identity (E) Reflection (s) Rotation (Rn) Rotation-reflection (Sn) Inversion (i) In periodic crystal lattice : (i) Additional symmetry - Translation (ii) Rotations – limited values of n
a a a n 3 2 1 0 -1 qo180 120 90 60 0 Rotation 2 3 4 6 1 Restriction on n-fold rotation symmetry in a periodic lattice q q na (n-1)a/2 cos (180-q) = - cos q = (n-1)/2
Crystal Systems in 2-dimensions - 4 square oblique hexagonal rectangular
Crystal Systems in 3-dimensions - 7 Cubic Tetragonal Orthorhombic Monoclinic Triclinic Hexagonal Trigonal
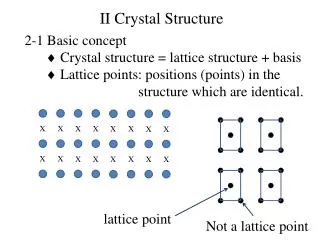
Bravais lattices in 2-dimensions - 5 square rectangular centred rectangular oblique hexagonal
Bravais Lattices in 3-dimensions (in cubic system) Body centred cube (I) Primitive cube (P) Face centred cube (F)
Bravais Lattices in 3-dimensions - 14 Cubic - P, F (fcc), I (bcc) Tetragonal - P, I Orthorhombic - P, C, I, F Monoclinic - P, C Triclinic - P Trigonal - R Hexagonal/Trigonal - P
Point group operations 7Crystalsystems Point group operations + translation symmetries 14 Bravais lattices
Lattice(o) + basis (x) = crystal structure
C4 Spherical basis C4 Non-spherical basis
Lattice+ SphericalBasis Lattice+ NonsphericalBasis Point group operations 7Crystalsystems 32 Crystallographic point groups Point group operations + translation symmetries 230 space groups 14 Bravais lattices
Miller plane in 2-D a a Distance between lines = a y (01) x (10)
Miller plane in 2-D Distance between lines = a/2 = 0.7 a y x (11)
Distance between lines = a/(2)2+(3)2 = 0.27 a Miller plane in 2-D (2, 3, 0) y Take inverses (23) x In 3-D: intercepts = 1/2, 1/3,
z y x Miller plane in 3-D (100) Distance between planes = a a
z y x Miller plane in 3-D (010) Distance between planes = a
z y x Miller plane in 3-D (110) Distance between planes = a/2 = 0.7 a
z y x Miller plane in 3-D (111) Distance between planes = a/3 = 0.58 a
a h2+k2+l2 dhkl = Spacing between Miller planes for cubic crystal system
Crystals • Waves • Bragg Law • Powder diffraction • Systematic absences, Structure factor • Single crystals - Solution and Refinement • Diffraction line width • Applications of powder diffraction
p 2p 0 0 l/2 l Phase Displacement l = wavelength u = frequency A = amplitude A sin{2p(x/l - ut)} sin (0) = sin (np) = 0 sin ([n+1/2]p) = +1 n even -1 n odd
Superposition of Waves amplitude = A amplitude = 2A Constructive interference
l/4 Superposition of Waves amplitude = A amplitude = 1.4A
Superposition of Waves l/2 amplitude = A amplitude = 0 Destructive interference
x 1 x+ l/2 2 x+ l 3 Waves 1 and 2 interfere destructively Waves 1 and 3 interfere constructively
Crystals • Waves • Bragg Law • Powder diffraction • Systematic absences, Structure factor • Single crystals - Solution and Refinement • Diffraction line width • Applications of powder diffraction
Wavelength =l q q d h k l h k l p l a n e q l 2 d s i n = n h k l
Crystals • Waves • Bragg Law • Powder diffraction • Systematic absences, Structure factor • Single crystals - Solution and Refinement • Diffraction line width • Applications of powder diffraction
Collection of several small crystals Single crystal Cones intersecting a film
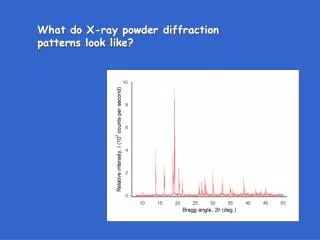
Powder x-ray diffractogram (sodium chloride) Counts 2q (degree)
NaCl - powder x-ray data source Cu-Ka (l = 1.540598 Å) Indexing a = d(h2+k2+l2)½
Crystals • Waves • Bragg Law • Powder diffraction • Systematic absences, Structure factor • Single crystals - Solution and Refinement • Diffraction line width • Applications of powder diffraction