Mechanical Ventilation
600 likes | 1.95k Vues
Mechanical Ventilation. Rob Stephens. Contents. Introduction: definition Introduction: review some basics Basics: Inspiration + expiration Details inspiration pressure/volume expiration Cardiovascular effects Compliance changes PEEP Some Practicalities. Definition: What is it?.

Mechanical Ventilation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mechanical Ventilation Rob Stephens
Contents • Introduction: definition • Introduction: review some basics • Basics: Inspiration + expiration • Details • inspiration pressure/volume • expiration • Cardiovascular effects • Compliance changes • PEEP • Some Practicalities
Definition: What is it? • Mechanical Ventilation =Machine to ventilate lungs = move air in (+ out) • Several ways to..move air in (IPPV vs others) Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation
Definition: What is it? • Mechanical Ventilation =Machine to ventilate lungs = move air in (+ out) • Several ways to..move air in (IPPV vs others) Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation • Several ways to ..connect the ventilator to the patient
Several ways to ..connect the machine to Pt • Oro-tracheal Intubation • Tracheostomy • Non-Invasive Ventilation
Definition: What is it? • Mechanical Ventilation =Machine to ventilate lungs = move air in (+ out) • Several ways to..move air in (IPPV vs others) Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation • Several ways to ..connect the machine to Pt • Unnatural- not spontaneous • consequences
Why do it?- indications • Hypoxaemia: low blood O2 • Hypercarbia: high blood CO2 • Need to intubate eg patient unconscious • Others eg • need neuro-muscular paralysis to allow surgery • want to reduce work of breathing • cardiovascular reasons
Review some basics • 1 Whats the point of ventilation? • 2 Vitalograph, lets breathe • 3 Normal pressures
Review 1 What’s the point of ventilation? • Deliver O2 to alveoli • Hb binds O2 (small amount dissolved) • CVS transports to tissues to make ATP - do work • Remove CO2 from pulmonary vessels • from tissues - metabolism
IRV VC TLC TV FRC ERV RV 0
Review 3: Normal breath Normal breath inspiration animation, awake Lung @ FRC= balance Diaghram contracts -2cm H20 Chest volume Pleural pressure -7cm H20 Alveolar pressure falls Air moves down pressure gradient to fill lungs
Review 3: Normal breath Normal breath expiration animation, awake -7cm H20 Diaghram relaxes Pleural / Chest volume Pleural pressure rises -2cm H20 Alveolar pressure rises Air moves down pressure gradient out of lungs
The basics: Inspiration Comparing with Spontaneous • Air blown into lungs • Different ways to do this • Air flows down pressure gdt • Lungs expand • Compresses • pleural cavity • abdominal cavity • pulmonary vessels
Ventilator breath inspiration animation Air blown in 0 cm H20 lung pressure Air moves down pressure gradient to fill lungs +5 to+10 cm H20 Pleural pressure
Ventilator breath expiration animation Similar to spontaneous…ie passive Ventilator stops blowing air in Pressure gradient Alveolus-trachea Air moves out Down gradient Lung volume
Details: Inspiration Pressure or Volume? • Do you push in.. • A gas at a set pressure? = ‘pressure…..’ • A set volume of gas? = ‘volume….’
Details: Inspiration Pressure or Volume? Pressure cm H20 Time Pressure cm H20 Time
Details: Expiration Pressure cm H20 PEEP Time Positive End Expiratory Pressure Pressure cm H20 PEEP Time
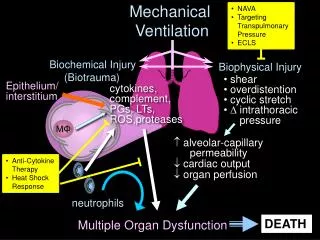
Details: Cardiovascular effects • Compresses Pulmonary vessels • Reduced RV outflow • Reduced LV inflow
Details: Cardiovascular effects • Compresses Pulmonary vessels • Reduced LV inflow • Cardiac Output: Stroke Volume • Blood Pressure = CO x resistance – Blood Pressure • Neurohormonal • Reduced RV outflow- backtracks to body • Head- Intracranial Pressure • Others - venous pressure
Details: Cardiovascular effects • Compresses Pulmonary vessels • Inspiration + Expiration • More pressure, effects on cardiovascular • If low blood volume • vessels more compressible • effects
Details: compliance changes • If you push in.. • A gas at a set pressure? = ‘pressure…..’ • Tidal Volume compliance • Compliance = Δvolume / Δpressure • If compliance: ‘distensibility stretchiness’ changes • Tidal volume will change • A set volume of gas? = ‘volume….’ • Pressure 1/ compliance • If compliance: ‘distensibility stretchiness’ changes • Airway pressure will change
Details: compliance changes Normal ventilating lungs
Details: compliance changes Abormal ventilating lungs: Eg Left pneumothorax
Effects of PEEP Normal, Awake • in expiration alveoli do not close (closing capacity) • change size Lying down / Paralysis / +- pathology • Lungs smaller, compressed • Harder to distend, starting from a smaller volume • In expiration alveoli close (closing capacity) PEEP • Keeps alveoli open in expiration • Danger: applied to all alveoli • Start at higher point on ‘compliance curve’
Effects of PEEP ‘over-distended’ alveoli Compliance= Volume Pressure Volume • energy needed to open alveoli • ?damaged during open/closing • - abnormal forces Pressure
Effects of PEEP Compliance= Volume Pressure Volume PEEP: start inspiration from a higher pressure ↓?damage during open/closing Pressure Raised ‘PEEP’
IRV VC TLC TV FRC Closing Capacity ERV RV 0
IRV VC TLC TV FRC Closing Capacity ERV RV 0
Regional ventilation: PEEP Spontaneous, standing ‘over-distended’ alveoli Compliance= Volume Pressure Volume Pressure
Regional ventilation: PEEP Mechanical Ventilation Compliance= Volume Pressure Volume Pressure
Practicalities • Ventilation: which route? • Intubation vs others • Correct placement? • Ventilator settings: • spontaneous vs ‘control’ • Pressure vs volume • PEEP? • How much Oxygen to give (Fi02 ) • Monitoring adequacy of ventilation (pCO2,pO2) • Ventilation: drugs to make it possible • Ventilation: drug side effects • Other issues
Practicalities • Ventilation: which route? • Intubation vs others • Correct placement? • Ventilator settings: • spontaneous vs ‘control’ • Pressure vs volume • PEEP? • How much Oxygen to give (Fi02 ) • Monitoring adequacy of ventilation (pCO2,pO2) • Ventilation: drugs to make it possible • Ventilation: drug side effects
Other reading • http://www.nda.ox.ac.uk/wfsa/html/u12/u1211_01.htm Practicalities in the Critically ill • http://www.nda.ox.ac.uk/wfsa/html/u16/u1609_01.htm