Nervous Regulation
170 likes | 380 Vues
Nervous Regulation. Brain. Organ of the Central Nervous It is the primary center for the regulation and control of bodily activities, receiving and interpreting sensory impulses, and transmitting information to the muscles and body organs. composed of gray matter and white matter. Neuron.

Nervous Regulation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Brain • Organ of the Central Nervous • It is the primary center for the regulation and control of bodily activities, receiving and interpreting sensory impulses, and transmitting information to the muscles and body organs. • composed of gray matter and white matter.
Neuron -a cell that is specialized to conduct nerve impulses
Cell Body • -contains the nucleus and cell organelles of a neuron, controls metabolic activity
Dendrites • -short, highly branched fibers that receive impulses. • Conduct impulses toward the cell body • Give the cell a “bushy” appearance
Axon • a long, thin fiber that extends from the cell body. • Carry impulses away from the cell body and send them either to other neurons or to effectors. • Range in length: 1 centimeter to 1 meter • Also called a nerve fiber.
Schwann Cells Form a covering around the axon and produce layers of a white, fatty substance called mylein.
Neuromuscular Junction The neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is the site of communication between motor nerve axons and muscle fibers. The function of the NMJ is to transmit signals from the motor neuron to the skeletal muscle fiber quickly and reliably, to ensure precise control of skeletal muscle contraction and therefore voluntary movement
Neurotransmitter -are the chemicals which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses
Sodium-Potassium Pump -the mechanism that uses ATP energy to reset the sodium and potassium ions after transmission of a nerve impulse.
Refractory Period -is when the Na+ and K+ are returned to their original sides: Na+ on the outside and K+ on the inside.
Threshold The minimum level of a stimulus required to activate a neuron
Nerve Net A diffuse network of cells that conducts impulses in all directions from the area stimulated, forming a primitive nervous system in coelenterates, and other simple organisms.
Irritability ability of a cell to respond to its environment is an excessive response to stimuli.
Ganglion -a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center, especially one located outside the brain or spinal cord
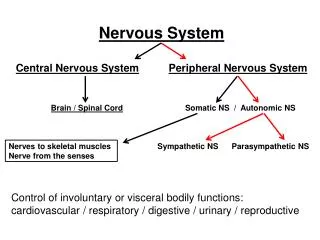
Central Nervous System -receives information from and sends information to the peripheral nervous system. - the two main organs of the CNS are the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System -the section of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord