action
100 likes | 311 Vues
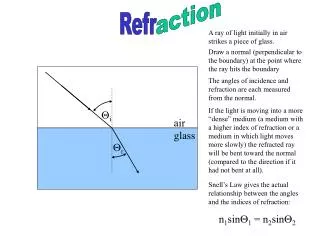
action. Refr. A ray of light initially in air strikes a piece of glass. Draw a normal (perpendicular to the boundary) at the point where the ray hits the boundary. The angles of incidence and refraction are each measured from the normal.

action
E N D
Presentation Transcript
action Refr A ray of light initially in air strikes a piece of glass. Draw a normal (perpendicular to the boundary) at the point where the ray hits the boundary The angles of incidence and refraction are each measured from the normal. If the light is moving into a more “dense” medium (a medium with a higher index of refraction or a medium in which light moves more slowly) the refracted ray will be bent toward the normal (compared to the direction if it had not bent at all). Qi air glass Qr Snell’s Law gives the actual relationship between the angles and the indices of refraction: n1sinQ1 = n2sinQ2
action Refr air quartz water diamond glass air n = 1.00 n = 1.46 n = 1.33 n = 2.42 n = 1.52 n = 1.00
action Refr Example Problem: Sketch the path of the Ray below as it passes into, And eventually out of the glass (the glass shape is an equilateral triangle) Use nglass= 1.52 to calculate the angles of incidence and refraction at each of the two boundaries. 60o 64.7o 40.5o 55.3o 25.3o 60o 34.7o 30o
Total Internal Reflection A ray of light under water strikes the water surface from underneath. Some of the ray reflects and stays in the water, some of the ray refracts out into the air. As the angle of incidence in the water gets larger, more of the light is reflected and less is refracted. When the angle of incidence gets big enough, the angle of refraction reaches 90o, and no light is refracted out of the water. This angle of incidence is called the critical angle. At any angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, no refraction occurs, only reflection. This process is known as total internal reflection. Qi Qi Qi Critical Angle
Total Internal Reflection Snell’s Law: n1sinQ1 = n2sinQ2 At the critical angle of incidence (Q1 = Qc), Q2 = 90o Therefore: n1sinQc = n2sin 90o sinQc = Qi Qi Qi Critical Angle
A ray of light enters a piece of glass. It refracts and reflects at the various boundaries. It eventually leaves the bottom surface coming out perpendicular to the base. • Answers: • 7) 55o • 5) 20o • 4) 20o • 6) 33.2o • 3) 15o • 1) 24.5o • 2)24.5o 35o 2 1 3 4 5 start 6 7 If the index of refraction for the glass is 1.60, determine angles 1 - 7.
action Refr DISPERSION The index of refraction of a material actually varies slightly with wavelength. Low frequency, long wavelength light (toward the red end of the color spectrum) has a smaller index of refraction, and therefore bends slightly less. The higher frequency, short wavelength light (toward the violet end of the color spectrum) bends more.