Stem Cells
230 likes | 521 Vues
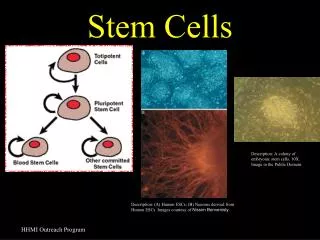
Stem Cells. Alex Cart Frank Cummings. Alright so what are they? 1. Stem cells are a class of undifferentiated cells that are able to differentiate into specialized cell types Able to reproduce themselves “Immortal” Basically, a blank canvas or pluripotent. 2. Video! 3.

Stem Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Stem Cells Alex Cart Frank Cummings
Alright so what are they?1 • Stem cells are a class of undifferentiated cells that are able to differentiate into specialized cell types • Able to reproduce themselves • “Immortal” • Basically, a blank canvas orpluripotent
Video!3 • http://www.kqed.org/quest/television/view/326?gclid=CJHosOa-_J8CFQdY2godthIRjw
And where do they come from?1 Embryos Adults
Embryos1 • They are undifferentiated blastocysts • Four to five days old • Super controversial • The baby hasn’t begun to form yet 4
Brain Bone marrow Blood Blood vessels Skeletal muscles Skin Liver Don’t divide until activated by disease or injury There is debate on what they will differentiate into Adult Stem Cells1
Process • The stem cells are put in a Petri dish atop a layer of “feeder cells” or cell cultures • Depending on what the type of cell the feeder cell is, the stem cell will form into that cell
Controversy1 • When does “life” start? • Are chimeras ethical? • Researchers use mouse embryos to create human stem cells • Not as controversial but still….
Current Treatments6 • Helps cancer patients • Skin grafts • Like the baby we read about
Brain damage Cancer Spinal cord injury Heart damage Haematopoiesis (blood cell formation) Baldness Missing teeth Deafness Blindness and vision impairment Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Graft vs. host disease and Crohn's disease Neural and behavioral birth defects Diabetes Orthopedics Wound healing Infertility Potential Treatments
Australia Canada China Most of Europe Finland Israel Japan Singapore United Kingdom Where else is it being done?7
References • http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/info/stem_cell/whatarestemcells.php • http://theblackcordelias.files.wordpress.com/2009/03/stem-cells.jpg • http://www.kqed.org/quest/television/view/326?gclid=CJHosOa-_J8CFQdY2godthIRjw • http://florenceblanchard.files.wordpress.com/2009/11/24stem6501.jpg • http://www.odec.ca/projects/2008/hess8s2/images/cell%20controversy.png • http://www.cellmedicine.com/?gclid=CJuX4ODv_p8CFeSL5wodlF4Hlw • http://stemcells.nih.gov/research/intlresearch.asp • http://www.mbbnet.umn.edu/scmap.html