Sheep Brain Dissection
160 likes | 321 Vues
Explore the fascinating world of the sheep brain, similar to the human brain, to uncover the intricate structures of memory, learning, and cognition. Discover the cortex, gray matter, and the divide between left and right brain functions. Unravel the secrets of how memories are stored and processed, offering invaluable insights into the workings of our own minds.

Sheep Brain Dissection
E N D
Presentation Transcript
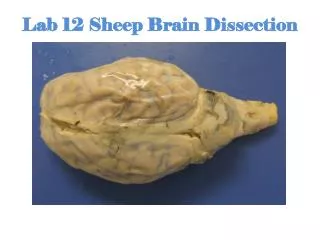
By dissecting the brain of a sheep, an animal in which brain structure and function are similar to our own, we can see where the learning processes take place.
The outer layer of the brain is the CORTEX, which means bark. Though it is only a few millimeters thick, the deep folds of the cortex contain 70% of a person’s one hundred billion brain cells. These cells are responsible for the highest level of thought and memory. With respect to body size, humans have the largest cortex of any animal.
GRAY MATTER The dark colored top of the cortex. It gets this color from the dark nuclei of the brain’s cell bodies.
The inner, lighter layer is called “white matter”. Running from the cell bodies are long white extensions called axons, which make up the brain’s white matter. The axon of each brain cell reaches out through the brain to make connections with other brain cells. It is through these connections that billions of brain cells relay information to billions of other brain cells creating a communication network that makes thought possible.
There are several main subdivisions of memory, each of which is processed in a different area of the brain. • Working memory happens at the front of the brain, in the prefrontal cortex. This type of memory coordinates long-term memories with sights, sounds, and feelings, so you can respond to events as they happen. • Long-Term memory accesses an amazing range of information—from knowledge of yourself to your understanding of the world. These are processed deep in the brain, in a spiral area called the hippocampus. This is Greek for, “seahorse.” This is where experiences become memories.
Dividing the sheep brain in half reveals the tree-like structure of the cerebellum. It is here, in one of the most primitive parts of the brain, that skilled memories are processed. Your cerebellum then passes this information on to the basal ganglia, which are responsible for storing skill memories and refining the coordinations and sequences of your movements.
The Cerebellum Tree-like design: Here is where skill memory is stored. From the act of tying your shoe to dancing the tango, skill memory helps you remember the activities you learn throughout your life.
More Questions • Studying sheep brains can help us better understand our own brains, yet they remain mysterious. • This mass of tissue can somehow take bits of information about life and store them selectively: • How are they stored? • Where are they stored?. • As in all great mysteries, the answers are out there, we just have to know where to look.