Motion 11.1 Distance and Displacement
490 likes | 1.22k Vues
Motion 11.1 Distance and Displacement. Chapter 11. What are we going to learn?. Methods of describing motion How can vectors be combined?. A story of motion.

Motion 11.1 Distance and Displacement
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Motion11.1 Distance and Displacement Chapter 11
What are we going to learn? • Methods of describing motion • How can vectors be combined?
A story of motion... • Once upon a time, 3 students (George, Harry, and William) were on their way to school. When asked the question, “How fast are your friends moving?” there were very different and conflicting answers from the students.
George says that Harry and William are moving very fast. • Harry says that George is moving but William is not. • William says that George is moving but Harry is not.
It’s all a matter of frame of reference... • Hint........
George is standing waiting at the bus stop. Harry and William are already on a moving bus.
Frame of Reference • Necessary to describe motion accurately and completely • A system of objects that are not moving with respect to one another
Relative Motion • Movement in relation to a frame of reference • More on this later.....
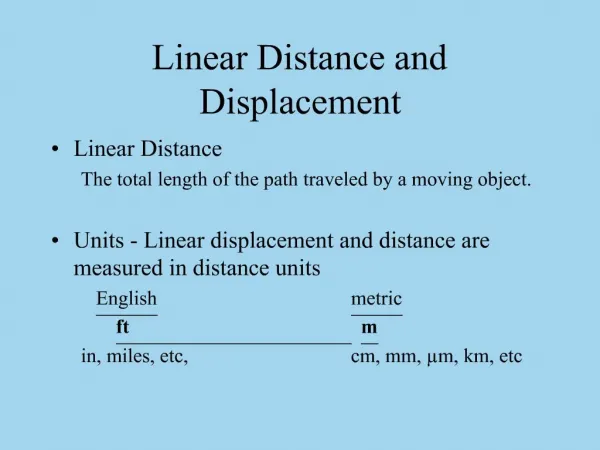
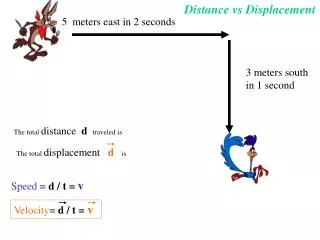
Distance • Length of the path between two points
Distance Units • SI unit for distance: meter (m) • For very large distances: kilometers (km) • For distances smaller than meters: centimeters (cm)
Displacement • Direction from the starting point and the length of a straight line from the starting point to the ending point • Gives information both about how far away an object is from a given point and in what direction the object is from that point • Displacement is a vector
Vectors • A quantity that has direction and magnitude (can be size, length, or amount) • Add displacements using vector addition
Vector Addition • When two vectors have the same direction, you can add their magnitudes
When two vectors are in opposite directions, subtract one magnitude from the other Ex: A police officer going the speed limit of 45 mph clocks you going in the opposite direction at 92 mph. Do you get a ticket?
Since the vehicles are going in oppositedirections, subtract the police officer vector from your vehicle vector...the answer is your unknown speed • 92 mph – 45 mph = 47 mph (2 mph over the speed limit)
When two or more vectors have different directions, combine them by graphing
Vector Addition • Sum of two or more vectors is the resultant vector
Review Questions • What two things must you know to describe the motion of an object?
Review Questions • What two things must you know to describe the motion of an object? Frame of reference and direction
True or false? A frame of reference is not necessary to describe motion accurately and completely.
True or false? A frame of reference is not necessary to describe motion accurately and completely. False, frame of reference is necessary to accurately describe motion
True or false? Five blocks south is an example of a displacement.
True or false? Five blocks south is an example of a displacement. True
Circle the letter of the SI unit best suited for measuring the length of a room in your home. a. kilometers b. meters c. centimeters d. millimeters
Circle the letter of the SI unit best suited for measuring the length of a room in your home. a. kilometers b. meters c. centimeters d. millimeters
Imagine that you are a passenger in a car. Circle the letter of the best frame of reference you could use to determine how fast the car is moving relative to the ground. a. the people sitting next to you in the backseat b. the driver of the car c. a van traveling in the lane next to your car d. a sign post on the side of the road
Imagine that you are a passenger in a car. Circle the letter of the best frame of reference you could use to determine how fast the car is moving relative to the ground. a. the people sitting next to you in the backseat b. the driver of the car c. a van traveling in the lane next to your car d. a sign post on the side of the road
What would your total displacement be if you walked from your front door, around the block, and then stopped when you reached your front door again? a. one block b. two blocks c. the entire distance of your trip d. zero
What would your total displacement be if you walked from your front door, around the block, and then stopped when you reached your front door again? a. one block b. two blocks c. the entire distance of your trip d. zero
Compare and contrast distance and displacement. Same: both describe measurement of motion Different: distance is a straight line measurement between 2 points displacement includes direction and a straight line measurement from starting point to finish point
A vector is a quantity that has both ______________ and ______________.
A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
The vector sum of two or more other vectors is called the _________________________.
The vector sum of two or more other vectors is called the resultant vector.
Circle the letter of each answer that could describe the magnitude of a vector. a. length b. direction c. amount d. size
Circle the letter of each answer that could describe the magnitude of a vector. a. length b. direction c. amount d. size
Because the two displacements are in opposite directions, the magnitude of the total displacement is ________________________ .
Because the two displacements are in opposite directions, the magnitude of the total displacement is addition of opposite vectors with a total displacement of 4 km.
Circle the letter that answers the question. What is the displacement of a cyclist who travels 1 mile north, then 1 mile east, and finally 1 mile south? a. 3 miles east b. 1 mile north c. 3 miles south d. 1 mile east
Circle the letter that answers the question. What is the displacement of a cyclist who travels 1 mile north, then 1 mile east, and finally 1 mile south? a. 3 miles east b. 1 mile north c. 3 miles south d. 1 mile east