Multiplying Polynomials: Essential Guide with Examples
240 likes | 268 Vues
Learn how to multiply monomials and polynomials using exponent properties. Practice examples included for better understanding. Find solutions to problems and sharpen your algebra skills.

Multiplying Polynomials: Essential Guide with Examples
E N D
Presentation Transcript
6-5 Multiplying Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt McDougal Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1
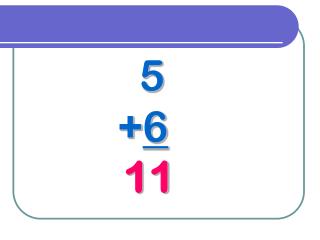
Warm Up Simplify and evaluate. 1. 7m2 + 3m + 4m2 2. (r2 + s2) – (5r2 + 4s2) 3. (10pq + 3p) + (2pq – 5p + 6pq)
Essenstial Question How do you multiply polynomials?
To multiply monomials and polynomials, you will use some of the properties of exponents that you learned earlier in this chapter.
Remember! When multiplying powers with the same base, keep the base and add the exponents. x2x3= x2+3 = x5
(6 3)(y3y5) (3 9)(m m2)(n2 n) Example: Multiplying Monomials A. (6y3)(3y5) (6y3)(3y5) Group factors with like bases together. Multiply. 18y8 B. (3mn2) (9m2n) Group factors with like bases together. (3mn2)(9m2n) 27m3n3 Multiply.
1 æ ö ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 s t t - 12 t s s ç ÷ 4 è ø 1 æ ö ( ) ( ) 2 2 • 2 s s s t t t • −12 • ÷ ç 4 ø è Example: Multiplying Monomials (st) (-12 s t2) s2 t2 1 4 Group factors with like bases together. • • Multiply.
(3 6)(x3x2) I do…. Multiply. a. (3x3)(6x2) Group factors with like bases together. (3x3)(6x2) Multiply. 18x5
(2 5)(r2)(t3 t) We do…. Multiply. b. (2r2t)(5t3) Group factors with like bases together. (2r2t)(5t3) Multiply. 10r2t4
1 ö æ ( ) ( ) 2 3 2 y 4 5 x y 12 x z z ÷ ç 3 ø è 1 ö æ ( ) ( ) ( ) y y 2 3 4 2 5 12 x x z z ÷ ç 3 ø è 5 5 7 4 x y z You do…. Multiply. 1 æ ö ( ) ( ) 3 2 4 5 2 c. x y 12 x z y z ç ÷ 3 è ø Group factorswith like bases together. Multiply. • • • •
Distribute 4. Example: Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial 4(3x2 + 4x – 8) 4(3x2 + 4x – 8) (4)3x2 +(4)4x – (4)8 Multiply. 12x2 + 16x – 32
Distribute 6pq. Example Multiply. 6pq(2p – q) (6pq)(2p – q) (6pq)2p + (6pq)(–q) Group like bases together. (6 2)(p p)(q)+ (–1)(6)(p)(q q) 12p2q –6pq2 Multiply.
1 1 ( ) Distribute . 2 2 2 x y xy 2 x y 6 + x y 8 2 2 1 ö æ ö æ 1 ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 x y 6 xy + x y 8 x y ÷ ç ÷ ç 2 2 ø è ø è ö æ ö 1 æ 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) •6 x2 •x + y •y •8 x2•x2 y •y2 ÷ ç ÷ ç 2 ø è ø 2 è Example Multiply. 1 ( ) 2 2 2 x y 6 + xy 8 x y 2 Group like bases together. 3x3y2 + 4x4y3 Multiply.
1. Multiply the First terms. (x+ 3)(x+ 2) x x= x2 2. Multiply the Outer terms. (x+ 3)(x+ 2) x 2= 2x 3. Multiply the Inner terms. (x+ 3)(x+ 2) 3x= 3x 4. Multiply the Last terms. (x+ 3)(x+ 2) 32= 6 (x + 3)(x + 2) = x2+2x + 3x +6 = x2 + 5x + 6 F O I L FOIL method. F O I L
Example: Multiplying Binomials (s + 4)(s – 2) (s + 4)(s – 2) s(s – 2) + 4(s – 2) Distribute. s(s) + s(–2) + 4(s) + 4(–2) Distribute again. s2 – 2s + 4s –8 Multiply. s2 + 2s –8 Combine like terms.
Helpful Hint In the expression (x + 5)2, the base is (x + 5). (x + 5)2 = (x + 5)(x + 5)
(x x) + (x (–4)) + (–4 x) + (–4 (–4)) Example: Multiplying Binomials Multiply. Write as a product of two binomials. (x –4)2 (x –4)(x – 4) Use the FOIL method. x2– 4x– 4x+16 Multiply. x2 – 8x + 16 Combine like terms.
(xx) +(x(–3)) + (–3 x)+ (–3)(–3) ● Example Multiply. Write as a product of two binomials. (x – 3)2 (x – 3)(x – 3) Use the FOIL method. x2 – 3x – 3x + 9 Multiply. x2 – 6x + 9 Combine like terms.
Example: Multiplying Polynomials Multiply. (x – 5)(x2 + 4x – 6) (x – 5 )(x2 + 4x – 6) Distribute x. x(x2 + 4x – 6) – 5(x2 + 4x – 6) Distribute x again. x(x2) + x(4x) + x(–6) – 5(x2) – 5(4x) – 5(–6) x3 + 4x2 – 5x2 – 6x – 20x + 30 Simplify. x3 – x2 – 26x + 30 Combine like terms.
A = l w A = l w Example 5: Application The width of a rectangular prism is 3 feet less than the height, and the length of the prism is 4 feet more than the height. a. Write a polynomial that represents the area of the base of the prism. Write the formula for the area of a rectangle. Substitute h – 3 for w and h + 4 for l. A = (h+ 4)(h – 3) Multiply. A = h2 + 4h– 3h – 12 A = h2 + h– 12 Combine like terms. The area is represented by h2 + h– 12.
Example 5: Application Continued The width of a rectangular prism is 3 feet less than the height, and the length of the prism is 4 feet more than the height. b. Find the area of the base when the height is 5 ft. A = h2 + h– 12 Write the formula for the area the base of the prism. A = h2 + h– 12 A = 52 + 5 – 12 Substitute 5 for h. A = 25 + 5 – 12 Simplify. A = 18 Combine terms. The area is 18 square feet.
Lesson Quiz: Part I Multiply. 1. (6s2t2)(3st) 2. 4xy2(x + y) 3. (x + 2)(x – 8) 4. (2x – 7)(x2 + 3x – 4) 5. 6mn(m2 + 10mn – 2) 6. (2x – 5y)(3x + y)
Lesson Quiz: Part II 7. A triangle has a base that is 4cm longer than its height. a. Write a polynomial that represents the area of the triangle. b. Find the area when the height is 8 cm.