Basic Functions and Their Applications in Biology: Fractals and Radioactive Decay
250 likes | 367 Vues
This lecture explores fundamental mathematical functions such as exponential, logarithmic, and power functions, and their applications in biological processes, particularly relating to the age determination of fossilized organic matter using carbon-14 dating. Key concepts include self-similarity in fractals, species-area relationships, and scaling laws in ecological contexts. The lecture also touches on branching processes and the relationship between population density and body weight, providing a mathematical basis for understanding biodiversity. Prepare for future topics including vector operations and matrix types.

Basic Functions and Their Applications in Biology: Fractals and Radioactive Decay
E N D
Presentation Transcript
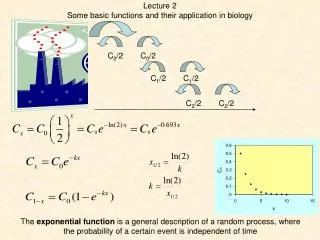
Lecture 2 Somebasicfunctions and theirapplicationinbiology C0/2 C0/2 C1/2 C1/2 C2/2 C2/2 Theexponentialfunctionis a general description of a random process, wheretheprobability of a certaineventis independent of time
C14 has a half time of 5568 years. How long would it take until of one mol C14 only one atom remains? One mol contains 6.0210*1023atoms
The age of fossilized organic matter can be determined by the C14-method of radioactive decay. The half-live of C14 is 5568 years. The equilibrium content of C14 in living plants is about 10-6ppm (parts per million). How old is a fossilized plant with a C14 content of 1.5*10-7ppm?
Thelogarithmicfunction Log-seriesrelativeabundancedistribution Species – area relation
Selfsimilarobjects The Sierpinski triangle • Start with a triangle, • shrink to 1/2 size, • make three copies • arrange the three copies in quadrants 2,3, and 4 • goto (2).
"All the branches of a tree at every stage of its height when put together are equalin thickness to the trunk„ (Leonardo da Vinci, Notebooks, 1510)
Scalingfactor = 1 / unit of measurement = magnification a iscalledthenormalizationconstant
Whatisthevalue of a? IfourobjectisclassicalEuclidean d = 0 Rulerlength l Bothequationsmatchif b = cs Now we consider an area. Theareascales to thesquare of therulerlength Bothequationsmatchif b = cs2
. Euclideandimension E=0 Euclideandimension E=1 Euclideandimension E=2 0 < d < 1 Euclideandimension E=3 E+dtakesalwaysvaluesbetweentheactualEuclideandimension and thenexthigher one. Itiscommonlytermedthefractaldimensionof an object. An importantclass of fractalobjectsareselfsimilarobjects. We describethem by powerfunctions.
What are the relation between radius, volumen and surface in such a branching pattern? A branchingpattern X = 0.75
Calculatethetotalleafarea of thisfern We have to measuretwoleafsatdifferentscale to getthescalingexponent of thearea - lengthrelationship Lettheaveragelength of thesmallestleaflets be 1 cm and itsarea 3 cm2. Atthenexthigherscaleleafletlengthmight be 10 cm and therespectivearea 35 cm2. Thewholefernis 1 m long.
How should population density scale to body weight? Populationdensityisproportional to availablespace and to available energy.
MD is proportional to total population biomass What is if z is about 0.75? Energy equivalence(Damuth’s) rule (for poikilotherms: equalbiomasshypothesis)
The mean number of bee species per km2 in Poland [312685 km2]is 110, the total number of Polish bees is 463. Estimate the number of bees in the district of Kujaw-Pommern [17970 km2]. Observed: unknown The mean number of bird species in Poland is about 430, the total European [10500000 km2] species number is about 800. How many species do you expect for France [543965 km2]? Would it make sense to estimate the species number of Luxembourg [2586 km2]? What about Kujaw-Pommern [17970 km2]? Observed: 530 Observed: 250 Observed: 262
The inverse hyperbola Michaelis-Menten equation Monod function
Haemoglobin or myoglobin bind oxygen according to the partial pressure of O2 Denoting y for [MbO], p(O2) for the partial pressure of oxygen and using [MbO] + [Mb] = const we get Hill equation of oxygen binding
Home work and literature • Refresh: • Fractal geometry • Selfsimilarity • Branchingprocesses • Logarithmictransformations • Species – arearelationships • Radioactivedecay • Prepare to thenextlecture: • Vectors • Vector operations (sum, S-product, scalarproduct) • Scalarproduct of orthogonalvectors • Distancemetrics (Euclidean, Manhattan, Minkowski) • Cartesian system, orthogonalvectors • Matrix • Types of matrices • Basic matrix operations (sum, S-product, dotproduct) Literature: Mathe-online Fractal geometry: http://classes.yale.edu/fractals/ Fractals: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fractal