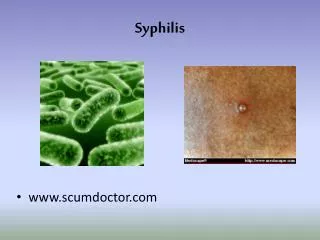
Syphilis
280 likes | 2.17k Vues
Syphilis. http://www.noooz.com/archives/gfxbin/2006/05/shocked.jpg. By: Chuan jia tran. http://www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~ytl/personal/images/Shocked.jpg. What is Syphilis?. Is a Sexual Transmitted Infection highly contagious

Syphilis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Syphilis http://www.noooz.com/archives/gfxbin/2006/05/shocked.jpg By: Chuan jia tran http://www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~ytl/personal/images/Shocked.jpg
What is Syphilis? • Is a Sexual Transmitted Infection • highly contagious - can be spread to another person through contact with a chancre on a person with syphilis generally by sexual activity [8]
Syphilis’s History • Been around for thousands of years [8] • Oldest trace found in the bones of a bear that lived 11,000 years ago [8] • Oldest trace in humans found in the remains of a human dating back 2,000 years ago. (signs of syphilis on remains; swollen leg bones, damaged skull) [8] • Most experts believe that Christopher Columbus and his crew brought the disease over to Europe from the Americas in 1493. [8] • Syphilis got its name from a poet/astronomer named Girolamo Fracastoro who had written a 1,300 verse poem about a myth of how the disease came to be. (poem titled “Syphilis, Sive Morbus Gallicus” in English it means “Syphilis, or the French disease”) [8] • Nick names…in the 16th century it was nicknamed “The Great Pox”, but others named it after their enemies for examples “The French Disease” or “the Neapolitan Disease” recent nicknames; “Bad Blood” “Syph” and “Miss Syph” [8]
Causes of Syphilis • caused by the bacteria Treponema Pallidum, spiral shaped, worm like. • There are several forms of syphilis, the most serious is the sexually transmitted • It burrows into the moist mucous membrane of human being’s mouths or genital area. - the mucous membrane is the soft skin found inside/around a person’s genital/anal/mouth area. • Goes through 4 stages, the symptoms of each stage worsens if the previous stage isn’t treated • Syphilis can potentially be fatal • coming in contact with an infected person’s chancres, the majority of the time through sexual activity. • Other treponemes cause milder infections http://www.uveitis.org/images/syphil1.jpg
The Effects and Symptoms of Syphilis • There are 4 stages of syphilis • At each stage the symptoms get worst • some infected people may not experience any symptoms at all
Stages of SyphilisPrimary Syphilis (first stage) http://www.dsu.org.uk/export/sites/Durham/image_gallery/storage/stithurs.jpg • Symptoms develop 10 days to 3 months within being infected [2] • Hard painless chancre sores [7] • The sore lasts between 3- 6 weeks, and after will disappear on its own • Most chancres appear around the genitals, mouth and areas that are hard to see [8] • Syphilis is highly contagious in this stage • The bacteria is multiplying in this stage http://www.sexualityandu.ca/images/sti/male_syphilis_e.jpg http://www.sexualityandu.ca/images/sti/syph_female_e.jpg
Stages of SyphilisSecondary Syphilis (second stage) • If left untreated there is a 30% chance that primary syphilis will progress into secondary syphilis • Symptoms of secondary syphilis can appear, even though symptoms such as chancres are still healing from the first stage • Symptoms are more serious • Can include fever; patchy hair loss; aching muscles and joints; swollen glands; sore throat; headaches; weight loss; lack of energy; rashes on the soles of the feet; palms of the hands, or elsewhere; and lesions on mucous membrane • If these symptoms are left untreated eventually it would go away but the disease is still in you • This stage is the most contagious • The bacteria has spread to the bloodstream http://www.scienceclarified.com/images/uesc_09_img0520.jpg http://www.psoriasiscafe.org/images/alopecia_areata_1.gif http://www.greatdreams.com/syphilis.jpg http://www.healthofchildren.com/images/gech_0001_0003_0_img0171.jpg
Stages of SyphilisLatent (third stage) • The latent stage begins when the symptoms of the second stage disappears • An illness is latent when its symptoms are hidden or invisible but the infection is still present inside the body • Syphilis can remain unnoticed for months to years if symptoms of the primary/secondary stages are left untreated • Infected people can still potentially spread the disease among other people • After roughly one year of latent syphilis, the disease stops being contagious http://www.myfirsttradeshow.com/Images/Smiley%20Face%20_Scared.jpg
Stages of SyphilisTertiary Syphilis (late/last stage) • The final stage of syphilis • About 25% of people with latent syphilis will experience the more serious damages [8] • the internal organs, the brain, the heart, nerves, eyes, liver, bone, joints, and blood vessels are possible damages that can be done [7] • Difficulty with coordinating muscle movements, numbness, paralysis, gradual blindness, and dementia [7] • curable but damages cant be repaired [3] • can lead to death http://www.utdallas.edu/~kilgard/brain.jpg http://www.iblog.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2007/09/humhrt2.jpg http://scotthull.files.wordpress.com/2007/01/scotts-liver-cropped.JPG
Congenital Syphilis • an unborn baby can be infected while in their mothers uterus if the mother is infected [2] • treatable before the 16th week of pregnancy the baby will most probably won’t be infected • 25-50% of pregnant women with syphilis suffer miscarriages [8] • 40% chance of a still birth (a still birth is a baby that is born dead) or the baby dies shortly after birth • 40 – 70% of babies with moms with syphilis contract the disease [8] • Babies with syphilis often have physical/mental development problems • Babies may suffer from blindness, deafness, abnormal bone growth, or mental retardation [2] http://www.medscape.com/content/1998/00/40/88/408881/art-wh3080.fig5.jpg http://services.epnet.com/GetImage.aspx/getImage.aspx?ImageIID=6170
Diagnosis of Syphilis • considered as the “great imitator” for its numerous symptoms [8] • Often difficult to diagnose syphilis just from symptoms of the first 2 stages • blood tests or • identifying bacteria from chancres or other sores with a microscope [8] http://depts.washington.edu/nnptc/online_training/std_handbook/gallery/images/treponemapallidum.jpg http://www.lifespan.org/adam/graphics/images/en/10026.jpg
The Treatments For Syphilis then • Earlier methods during the early 1500’s were bleeding, sweating, and vomiting (to get rid of the poisons in the body) substances such as mercury was used to provoke spitting and vomiting • Later that method was found useless now • Penicillin is the most efficient and is often used to treat syphilis [2] • Can cure it if earlier enough • Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered that killed micro organisms that infected humans with diseases • Can be taken as a pill or injection • Other treatment are available for patients who are allergic to penicillin • Can be infected again [3]
Future Outlook and Research • Curable • Can only be completely cured right now if caught early • The only thing that can be possibly done right now is stop it from spreading
How You Can Prevent Getting/Spreading Syphilis http://thephoenix.com/secure/uploadedImages/The_Phoenix/Life/Lifestyle_Features/RING_waitinside.jpg • Be abstinent • Don’t have sex relationships with tons of people • Don’t come in direct contact with sores, chancres, rashes. • Get tested occasionally if you are sexually active. • If you’re pregnant get tested to prevent transferring the disease • If you think you might have contracted syphilis, get tested • Tell your sexual partners that you have syphilis • And get it treated http://www1.istockphoto.com/file_thumbview_approve/816436/2/istockphoto_816436_colorful_condoms.jpg
Reference page • _______. (2002) Syphilis. Health Matters! (Vol.7 pp. 96-99). Danbury, Connecticut: Groiler. • Arno, Janet N. (2006). Syphilis. World Book (So-Sz Vol 18 pp. 1069). Chicago: World Book, inc. • Department of health and human services Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2008, January 4). Retrieved April 13, 2008 from the world wide web: http://www.cdc.govs/std/syphilis/STDFact-Syphilis.htm. • Familydoctor. (Dec. 2005). Retrieved April 13, 2008 from http://familydoctor.org/online/famdocen/home/common/sexinfections/sti/380.html. • Kids Health for Parents. (Aug. 2007). Retrieved April 13, 2008 from http://kidshealth.org/parent/infections/bacterial_viral/syphilis.html. • U.S. Department of Health of Health & Human Service. (May 2005). Retrieved April 13, 2008 from http://4woman.gov/FAQ/stdsyph.htm. • Younger-Lewis, Catherine. (2001). Syphilis. Canada Medical Association. (pp. 766). Toronto; Touraline Editions inc. • Winter, Adams. (2007). The Library of Sexual Health Syphilis, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.