A2 Unit 4 Revision Mindmaps
60 likes | 220 Vues
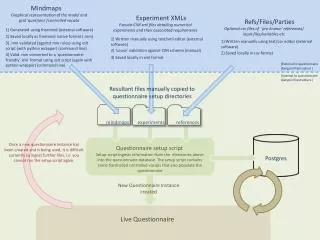
A2 Unit 4 Revision Mindmaps. Cognitive model - RP model. Behavioural (Learning) model -classical cond. -operant cond. Media Influences. Personality Peers Age Stress. Initiation Maintenance Relapse. Biological model Genes Twins Pathways VTA-NA + MDP. 2. Vulnerability to

A2 Unit 4 Revision Mindmaps
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cognitive model -RP model Behavioural (Learning) model -classical cond. -operant cond. Media Influences Personality Peers Age Stress Initiation Maintenance Relapse • Biological model • Genes • Twins • Pathways • VTA-NA + MDP 2. Vulnerability to addiction 1. Models of addictive behaviour Addictive Behaviour 3. Reducing addictive behaviour Models of prevention Types of intervention Public Health + legislation TPB/ HBM Biological psychological
The VTA-NA ‘common reward’ pathway “Addicted” Brain Prefrontal cortex (PFC) Part of the frontal lobe that is involved in many cognitive functions, including memory, language and decision making. Striatum MDP Pathway Nucleus Accumbens–(NA) A small region in the forebrain with ancient evolutionary origins, which helps regulate survival drives like food and thirst. Affected by drugs including cocaine, amphetamine, cannabinoids (e.g cannabis) and opioids (e.g. heroin). Ventral Tegmental Area– (VTA) Found in the midbrain, this area produces dopamine and forms part of one of four major dopamine pathways in the brain. Affected by drugs including; nicotine, alcohol and opioids (e.g. heroin). Dopamine movement Amygdala
24 mkUnit 3 A2 Psychology questions . . . PEE – used effectively to fully explain points Define terms (e.g. Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) properly A01 8marks 12 marks 4 marks Research support – used to back up points made Issues/debates – integrated into discussion e.g. nature versus nurture Your points = Connect points in your discussion Use scientific language - e.g. “supported by,” “criticised by,” A02 Mention AO3 terms (e.g. reliability, validity, reductionism, etc) A03
Biochemistry Genetics Cognitive Reliability & Validity Behavioural Biological explanations Classification & Diagnosis Psychological explanations Clinical characteristics Psychodynamic Schizophrenia Socio-cultural Psychological Therapies Biological Therapies ECT Psychosurgery Family Therapy CBT Drugs Genetics
Main features of science - replicability Peer review Selection & application of appropriate research methods Reliability Validity Ethics Scientific process -Popper -Kuhn 2. Designing investigations 1. Application of scientific method A2 Research Methods Statistical testing -effective selection 3. Data analysis & reporting of investigations Graph selection Probability Inferential tests -Spearmans Rho -Mann Whitney -Whilcoxon -Chi Squared Conventions of reporting on investigations Significance Type 1 & 2 errors