Cosmology
680 likes | 911 Vues
Cosmology. Cosmology- the study of the origin, present, and future of the universe. http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/gr/public/bb_cosmo.html. Einstein and Gravity.

Cosmology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cosmology- the study of the origin, present, and future of the universe.
Einstein and Gravity Rather than thinking of gravity as an attractive force between two objects (Isaac Newton) Einstein’s idea was that gravity is a property of massive objects that “bends” space and time around itself. Consider this- why doesn’t the Moon fly off into space, rather than staying in orbit around Earth? Newton would say gravity holds it in orbit. Einstein would say that the massive Earth “bends” space and time around itself, so that the moon follows the curves created by the massive Earth. His theory was confirmed when he predicted that even starlight would bend when passing near the sun during a solar eclipse.
But, even Einstein was wrong sometimes. He also came up with an idea he called the cosmological constant- it says the universe is static. It never changes and is the same everywhere. Free for commercial use from : http://www.easyvectors.com/browse/other/einstein-vector-material
1920: Harlow Shapley Finds Our Place in the Milky Way Shapley actually measure our universe. He found it to be About 100,000 light-years across. http://members.efn.org/~jack_v/Universe.html Shapley also helped us find out about nebulae. He catalogued About 2,500 of them. But, he thought they were all in our own galaxy! Today we call many of these galaxies! http://cosmology.carnegiescience.edu/timeline/1920
Then, beginning in 1929, Edwin Hubble made three very important discoveries • There are other galaxies besides the Milky Way • Many of these galaxies are moving away from us, thus the universe is expanding • The farther a galaxy is shifted to the red end of the spectrum, the faster it is moving away; thus, the farthest objects are the oldest objects. • People began to wonder- where did they come from?????
While looking through the telescope, Hubble discovered a Cepheid variable. Over the next several months Hubble determined that the star varied in brightness with a period of 31.45 days, which meant it was 7,000 times brighter than the Sun. Comparing its apparent brightness with its actual brightness Hubble determined that it was 900,000 light years away!
After The ‘Great Debate’ • After resolving the ‘Curtis-Shapley’ debate. Hubble measured the distance to Cepheid variable stars in the Andromeda Galaxy: • 2.5 million light years! Hmm...Much further than I suspected! I also noticed something else…..
Moving Galaxies • Hubble’s observations showed that the light from distant galaxies was ‘red-shifted’. This was due to the ‘Doppler Effect’. Light from distant galaxies Light from the Sun By Golly, just look at that! The dark lines in the spectrum on the right hand side are ‘red shifted’.
Recession Velocity • Hubble also noticed that the further away the galaxy, the greater the red-shift. The greater the red-shift the greater the speed of recession. My startling conclusion was that the further away the galaxy, the faster is was moving. Amazing! It also led me to develop what later became known as Hubble’s Law. After Me!
Hubble’s Law • The red-shift of distant objects is easy to measure therefore the recession velocity can also be easily calculated. • We can use the recession velocity to calculate the distance to a galaxy (or the velocity if the distance is known). This is known as Hubble’s Law. • The value of the Hubble Constant is 2x10-18 s-1(this value is still being researched). • E.g. A galaxy is 1.5 x 1020 km away. How fast is it moving? • Recession Velocity = Hubble Constant x 1.5 x 1020 • = 2x10-18 x1.5 x 1020 = 300 km/s Speed of recession (m/s) = Hubble Constant (s-1) x distance (km)
In the early 1900s a Belgian Priest by the name of Georges LeMaitre began studying Einstein’s laws of gravitation. He thought if they were true then the universe must be expanding. http://www.charleroi.be/anglais/ehisto_1.htm
In 1927, two years before Hubble’s discoveries, LeMaitre graduated from MIT with his PhD. He also wrote a paper stating that the universe is the same in every direction, but it is not static. He was ignored.
http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/astronomy/arny/student/webtutor/cosmological_red_shift/http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/astronomy/arny/student/webtutor/cosmological_red_shift/ LeMaitre used Hubble’s red shift discoveries as evidence for his own theory. He imagined the universe as a movie- only he played it backwards.
If indeed we played the movie backwards, then everything would come together into one single , small point- a primordial atom which held all matter.
The Big Bang Theory was born! Georges LeMaitre believed the universe must have begun in that primordial atom. Something then caused it to explode into the ever expanding universe we have today. If that explosion did occur, wouldn’t there be some radiation left today? People began to pay attention although not all believed LeMaitre’s theory to be true. Some information obtained from : www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/databank/entries/dp275i.html
Opposition to the Big Bang The Steady State Theory!
In 1948, Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold, and Sir Fred Hoyle proposed a different idea. They got the basis of their idea from a horror movie! Hoyle believed that as the universe expanded, the density of matter stayed the same because new matter was continuously being created. So, even though it was expanding, it was staying the same. www.schoolobservatory.org.uk/study/sci/cosmo/internal/steady.htm
http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/astronomy/hoyle_obit_010822.htmlhttp://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/astronomy/hoyle_obit_010822.html Sir Fred Hoyle Mathematically this can work IF the universe is the same in the past, the present, and the future. The Steady State Theory www.schoolobservatory.org.uk/study/sci/cosmo/internal/steady.htm
http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/astronomy/hoyle_obit_010822.htmlhttp://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/astronomy/hoyle_obit_010822.html Sir Fred Hoyle Although Fred’s theory is probably not correct, he did help us figure out something else extremely important- how elements heavier than helium were created. He also came up with the name- Big Bang. He didn’t mean it nicely.
Then Quasars were discovered- 1963! Quasi-stellar radio source. They look like stars, but they can’t be stars because they are too bright and too far away. These were some of the most distant and brightest objects ever detected. Maarten Schmidt discovered one that was 1 billion LY away! The universe just keeps getting bigger. In the 1930s Grote Reberactually found the first quasar. He didn’t know it, but he had discovered even more evidence for the Big Bang and proof the Steady State Theory was not correct. http://cosmology.carnegiescience.edu/timeline/1966/quasar
Quasars • Very small • Very bright • Very far • Very old • Universe can’t be the same in the past, now, and future!
A few lucky mistakes lend even more evidence to the Big Bang Theory • In 1932, Carl Jansky, a Bell employee, accidentally discovered radio astronomy while looking for interference in radio telephone lines.
A few lucky mistakes lend even more evidence to the Big Bang Theory 2. In 1965, two more Bell employees tried to find the source of interference. This time it was microwave interference. ( They thought it was caused by pigeon poop, so they got rid of all of the pigeon nests.) They found the source- it was coming from everywhere in space.
In 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson had discovered : COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND RADIATION! This is the radiation leftover from the Big Bang explosion that scientists had been looking for! They won a Nobel Prize in 1978 for their discovery. Poor pigeons!
Another Strike against the Steady State Theory
Cosmic Background Radiation In 1965, the year that the CMB was discovered, a front-page story in the New York Times quoted Arno Penzias suggesting an activity that you can do today: “If you get a very good FM receiver and if you get between stations you will hear that sh-sh-sh sound. You’ve probably heard this kind of rushing sound. It’s just sort of soothing. Sometimes it’s not much different form the sound of the surf. Of the sound that you’re listening to, about one half of one percent of that noise iscoming from billions of years ago.”
Now What? http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/cosmology.html
Since the discovery of background radiation we have made tremendous strides in cosmology. We have since mapped the radiation throughout the universe with the Cosmic Background Explorer- COBE. The Big Bang theory is now accepted as standard cosmology.
The COBE has mapped subtle temperature differences in the radiation leftover from the Big Bang. These can be attributed to our sun, our galaxy, and some other influences. Blue- absolute zero (0K) Red- 4 degrees Kelvin (4K) Background radiation- 2.725 degrees Kelvin ( 2.725K) http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/m_uni/uni_101Flucts.html
Dark Matter There’s still much to learn! In 1978, Vera Rubin and a colleague set out to measure the mass of a galaxy. Little did they Know they were about to make the next BIG discovery. They fund the masses of some galaxies to be way too big- sometimes 10x too big. There had to be something else there- dark matter! http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/news/dark_matter_ring_feature.html
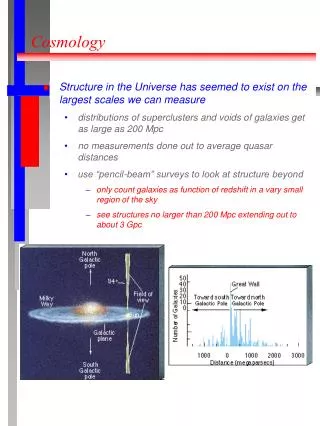
Mapping the Universe There’s still much to learn! In 1989, we began mapping the universe. Margaret Geller and John Huchra began the quest to map the Universe. Let’s see how far we’ve come. http://www.sdss.org/includes/sideimages/orangespider.html
1992 , Smoot and Mather show that slight differences in temperature found with COBE could create the galaxies and stars we see today. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosmic_Background_Explorer