Celiac disease
210 likes | 704 Vues
Celiac disease. What is Celiac Disease?. An autoimmune disease where the protein gluten damages the villi in the small intestine causing malabsorption. Celiac Disease is a lifelong condition. Celiac Disease is also called celiac sprue, nontropical sprue, and gluten sensitivity enteropathy.

Celiac disease
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is Celiac Disease? • An autoimmune disease where the protein gluten damages the villi in the small intestine causing malabsorption. • Celiac Disease is a lifelong condition. • Celiac Disease is also called celiac sprue, nontropical sprue, and gluten sensitivity enteropathy
What is gluten? Protein found in barley, rye, and wheat (includes spelt, kamut, and triticale)
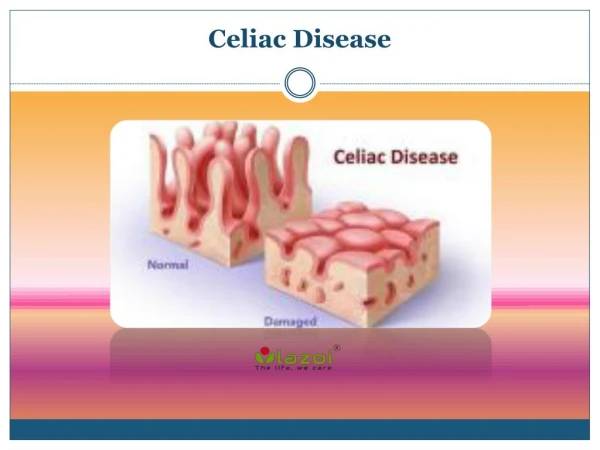
What causes Celiac Disease? • Immune system overreacts to gluten • Inflammation of mucosa in small intestine • Unknown cause, still being researched
What are the symptoms? Classic Symptoms • Abdominal distention/Bloating • Diarrhea • Stomach cramps • Gas • Constipation • Fatty stools
What are the symptoms (cont.) Less Obvious Symptoms • Fatigue • Joint pain • Bone loss • Depression • Weight loss • Neuropathy • Skin rash • Mouth ulcers • Missed menstrual cycles • Infertility
Symptoms in Children • Diarrhea or constipation (or both) • Failure-to-thrive • Stunted growth • Poor appetite or food aversion • Vomiting • Abdominal distention or bloating • Fatigue and irritability • Weight loss • Iron deficiency anemia • Behavior changes • Enamel defects of permanent teeth • Delayed puberty photo courtesy of Columbia University
How common is Celiac Disease? • 1 in 133 people are diagnosed with Celiac Disease • 97% of people with Celiac Disease are not diagnosed! • Prevalence of Celiac Disease has increased in the past 50 years • Can be misdiagnosed as IBS, Crohn’s, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, parasitic infection, or other bowel disorder
Who is at risk? Those diagnosed with: • Type 1 Diabetes • Autoimmune Thyroid condition • Rheumatoid Arthritis • Sjögren’s Syndrome • Addison’s disease • Down syndrome • Microscopic colitis • Autoimmune liver disease or hepatitis
How is Celiac Disease diagnosed? • Endoscopy with Intestinal Biopsy • Specific antibody blood tests • Capsule Endoscopy (Camera Pill) – least common
How is Celiac Disease diagnosed? Endoscopy and Biopsy Normal Celiac American Academy of Family Physicians www.aafp.org
When is Celiac Disease diagnosed? • Elevated anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies (tTGA) or anti-endomysium antibodies (EMA) via blood test • Damaged villi (villous atrophy) via biopsy • Celiac Disease can be diagnosed at any age • The longer Celiac Disease goes undiagnosed, risk increases for complications
Additional complications • Deficiencies of Iron, Folic Acid, B-12, calcium, and fat soluble vitamins • Lactose intolerance • Increased risk of GI cancers • Nervous system disorders • Pancreatic insufficiency • Bone loss
How is Celiac Disease treated? • No cure • Strict adherence to Gluten-Free(GF) Diet for life • If nutrient deficiencies exist, vitamin supplements will be needed • In severe cases, anti-inflammatory drugs may be needed to combat intestinal inflammation • New celiac patients should consult with a dietitian about a GF diet plan
What is the GF Diet? Strict Avoidance of all products containing wheat, including wheat bran, wheat germ, semolina, durum, enriched flour, and farina, rye, and barley, including barley malt and malt While oats are technically gluten-free, they are commonly contaminated with gluten unless tested and labeled as gluten-free oats
What is the GF Diet? Special care must be taken to avoid gluten in soups, seasonings, sauces, snack foods, processed meats, condiments, and beverages. Some restaurant chains have GF menus available.
Living with Celiac Disease • With strict adherence to GF Diet, intestinal damage can be healed • Intestinal healing takes 3 to 6 months in children • Healing will take years in adults • If improvement is not seen, diet should be investigated for hidden sources of gluten • Celiac disease is genetic • Long-term follow up is recommended
Sources (2008). Celiac disease (NIH Publication No. 08–4269). Retrieved from National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse website: http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/celiac (2011). Celiac disease. Retrieved from Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research website: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/celiac-disease/DS00319 Celiac Disease Foundation. (2010). Are You the One? [brochure]. Retrieved from http://www.celiac.org/images/stories/PDF/are-you-the-one.pdf
Sources (cont.) Celiac Disease Foundation. (2010). Is Your Child the One? [brochure]. Retrieved from http://www.celiac.org/images/stories/PDF/is-your-child-the-one.pdf Presutti, R. J. (2007). Celiac disease. American Family Physician, 76(12), 1795-1802. Retrieved from http://www.aafp.org/afp/2007/1215/p1795.html