A four function ALU
30 likes | 323 Vues
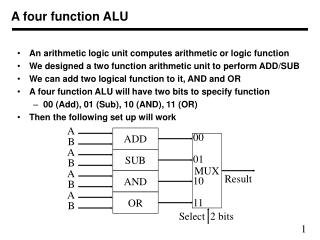
00 01 10 11. MUX. A. A. A. A. ADD. SUB. OR. AND. B. B. B. B. Result. Select 2 bits. A four function ALU. An arithmetic logic unit computes arithmetic or logic function We designed a two function arithmetic unit to perform ADD/SUB

A four function ALU
E N D
Presentation Transcript
00 01 10 11 MUX A A A A ADD SUB OR AND B B B B Result Select 2 bits A four function ALU • An arithmetic logic unit computes arithmetic or logic function • We designed a two function arithmetic unit to perform ADD/SUB • We can add two logical function to it, AND and OR • A four function ALU will have two bits to specify function • 00 (Add), 01 (Sub), 10 (AND), 11 (OR) • Then the following set up will work
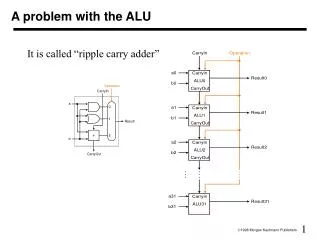
0 1 Add/sub MUX A A A OR AND ADD/SUB B B B 0 1 MUX Result Select0 Select1 An alternate design of four function ALU • The previous design is not very efficient as it uses an adder and subtract circuit • We can design an add/subtract unit as discussed earlier • Then we can design a logical unit (AND and OR) separately • Then select appropriate output as result • What are the control signals, Add/Sub, Select0, and Select1?
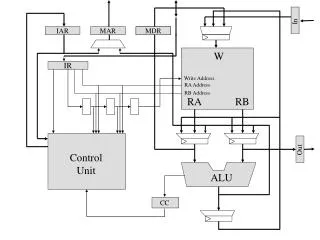
Operation codes • In micro-controllers, ALU units have many function • 16 arithmetic, 16 logic functions are common • A 5 bit code decides what function is required • This is part of an operation code in an instruction • Selection of operands is also specified as part of instruction • In actual instruction execution, operands A and B are first selected from different registers • Then different functions are computed • Finally, a result based on operation code is selected • This sequence is repeated for every instruction