Latent Heat and Phase Changes
160 likes | 315 Vues
Dive into the world of phase changes with this informative guide on the basic principles of boiling, freezing, melting, and latent heat. Discover how energy affects the transformation of matter between solid, liquid, and gas phases.

Latent Heat and Phase Changes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
3 Phases of Matter • Solid, Liquid, and Gas • Water can transfer from one phase to the next if you simply add or remove energy (heat)
Boiling • Boiling is when a liquid is changing phase to a gas (vaporization). • Addition of Heat
Boiling Point • A particular temperature that a substance boils. • Water = 212F and 100C
Freezing • When a liquid changes phases to a solid.
Freezing Point • A temperature at which a substance Freezes Water = 32F and 0C
Melting Point • Temperature at which a substance Melts from Solid Liquid • Ice = 32F and 0C
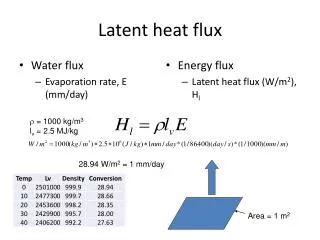
Latent Heat during Phase change • The energy used to change the phase of the material.
There is no temperature change on graph yet, heat is put into the material. The heat is absorbed by molecules to change phase. Where does the heat go?
Latent Heat • Two types of latent heat • Heat of fusion • Heat of vaporization
Heat of Fusion • Is the heat required to change a solid into a liquid. • Melting
Heat of Vaporization • Heat used to change a liquid to a gas. • Evaporation or boiling
Latent Heat (ESRT pg. 1) • Latent Heat is gained (absorbed) during melting (334 Joules/gram) • Latent Heat is released during freezing (334 Joules/gram) • Latent Heat is gained (absorbed) during vaporization (2260 Joules/gram) • Latent Heat is released during condensation (2260 Joules/gram)