Mechanical Waves
270 likes | 601 Vues
Mechanical Waves. Mechanical Waves. In mathematics and science , a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time , usually accompanied by the transfer of energy . What are mechanical waves?.

Mechanical Waves
E N D
Presentation Transcript
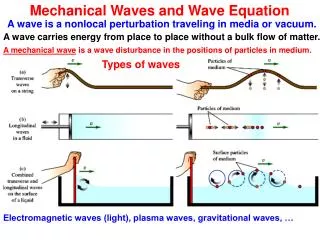
Mechanical Waves In mathematicsandscience, a wave is a disturbance that travels through spaceandtime, usually accompanied by the transfer ofenergy.
What are mechanical waves? • A mechanical waveis a disturbance in matter that carries energy from one place to another.
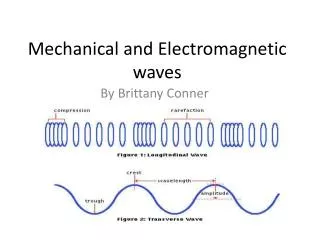
3 Main Types of Mechanical Waves • Transverse • Longitudinal • Surface
Transverse Waves • A transverse wave causes the medium to vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels.
Transverse Waves • A transverse waveis a wave in which particles of the medium move in a direction perpendicular to the direction that the wave moves
Shaking one end of a rope up and down creates Transverse Waves
Check for understanding…. • Move a rope up and down and observe the waves. • How does the direction of the wave compare with the direction in which the rope moves? • Create a human wave like at a ball game. • How does the direction of the wave compare with the direction in which the wave moves? • In a transverse wave , the particle motion is perpendicular to the direction of the wave velocity. A transverse wave may be created by shaking one end of a rope up and down or side to side. One example is a ripple on a pond.
Longitudinal Waves = • A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction of the wave. parallel circuit parallel port parallel planting
Check for Understanding:What are compressions and rarefactions in Longitudinal Waves?
Surface Waves Surface waves are combinations of transverse and longitudinal waves. These waves occur at the surface between two mediums, such as water and air. Up-and-down motion combines with back-and-forth motion. The combination produces circular motion.
Surface Wave A surface wave is a wave that travels along a surface separating two media.
Asurface wave is a wave that travels along a surface separating two media, such as water and air. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7yPTa8qi5X8
Check for UnderstandingSurface Waves Where do surface waves occur? • …at the surface between two mediums. • How do surface waves move? • …up and down like a transverse wave on a rope, and back and forth like coils in a spring.
Vocabulary: Properties of Mechanical Waves • The wavelength, λis the distance from any point on the wave to the adjacent point(one complete wave). • The amplitude of a wave is the maximum height of the wave. The amplitude does not affect the wave speed. • The frequency, Hzof a wave is the number of oscillations of cycles during an amount of time, usually a second. Frequency is measured in Hertz. One hertz is one cycle per second. • The periodof a wave is the time it takes for the wave to travel a distance of one wavelength.
Summary • http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/physics/basic_waves_theory.html
Wave examples which illustrate the definitionshttp://paws.kettering.edu/~drussell/Demos/waves-intro/waves-intro.html