Understanding Keratitis: Types, Causes, and Management
170 likes | 420 Vues
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, causing pain and vision impairment. Learn about different types, causes, signs, symptoms, and management options including antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal therapies, alongside nursing interventions and assessments.

Understanding Keratitis: Types, Causes, and Management
E N D
Presentation Transcript
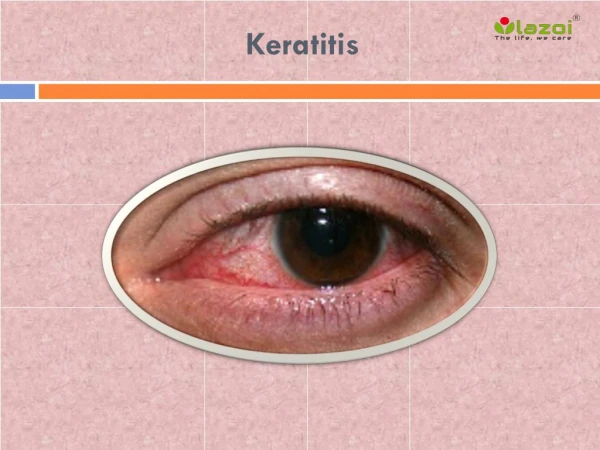
Keratitis • Inflammation of cornea characterized by moderate to intense pain and impaired vision
Types • Superficial keratitis – involves the superficial layers of the cornea and not generally leave a scar • Deep keratitis – deeper layers of the cornea (bowman’s membrane and other deep layers) and leave a scar that impairs vision
Causes Based on pathogens Amoebic keratitis – • Usually affecting contact lens wearers • Caused by acanthamoeba (acanthamoebakeratitis)
Bacterial keratitis– staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa • Fungal keratitis– aspergillus Viral keratitis- HSV • Dendritickeratitis or herpes simplex keratitis – usually leaves a dendritic ulcer • Herpes zoster keratitis – herpes zoster virus
Exposure keratitis– due to dryness of the cornea caused by incomplete or inadequate eyelid closure (in exophthalmos or masses inside the globe) • Photokeratitis – keratitis due to intense ultraviolet radiation exposure
Signs and symptoms • Pain • Tearing • Redness and blurring of vision • The pain may be mild to severe, depending on the cause and extent of the inflammation • Sensitivity to light may also be present
Management Antibacterial therapy • Topical antibiotics, subconjunctival antibiotic injection or in severe cases – IV antibiotics • Sub conjunctival injection – 25 G needle and 2 ml syringe.
Antiviral therapy – topical acyclovir • analgesics for pain • Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation Antifungal therapy • Natamycin– antifungal eye drop is the only treatment for acanthamoebakeratitis. Because all other drugs are resistant to acanthamoeba • If that treatment fails – keratoplasty
Nursing management for eye inflammations and infections Assessment -Assess ocular changes – • Edema • Redness • Decreasing visual acuity, • Feeling of foreign body • Discomforts
Nursing diagnosis • Acute pain related to irritation or infection of the eye • Anxiety related to outcome of treatment • Disturbed sensory perception (visual) related to diminished vision • Knowledge deficit
Interventions Health promotion • Aseptic technique • Frequent thorough hand washing – to avoid spreading • Dispose contaminated dressings • If the patient is having any STD’s, they are more risky
Apply warm or cool compresses if indicated • Darkening the room and providing appropriate analgesic – comfort measures • If the patient receives one or more eye drops – proper spacing should be given in between dosages – help and promote maximum absorption
Teach family regarding the safety measures and medication techniques • Do not share eye cosmetics • Do not share contact lens • Clean the contact lens properly and store it in a closed container.