Visual Basic
160 likes | 629 Vues
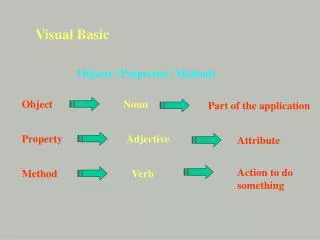
Visual Basic. Michael Harper Jasen Michalski Mark Hudson. Problem Domain. Problem Domain. Visual Basic was derived from BASIC Enables rapid application development of GUI applications, access to databases, and creation of ActiveX controls and objects.

Visual Basic
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Visual Basic Michael Harper Jasen Michalski Mark Hudson
Problem Domain • Visual Basic was derived from BASIC • Enables rapid application development of GUI applications, access to databases, and creation of ActiveX controls and objects. • Microsoft stopped supporting Visual Basic in 2005, focusing on Visual Basic .NET.
Problem Domain (ctd.) • Visual Basic.NET is an evolution of Visual Basic, implemented on the Microsoft .NET framework. • Because of the .NET architecture earlier versions of Visual Basic had to be re-written before they could be used with .NET • Visual Basic.NET dropped the .NET from it’s name in Visual Basic 2005.
Problem Domain (ctd.) • Vista will run Visual Basic 6 programs, but Microsoft does not sell Visual Basic 6 anymore. They are encouraging users to switch to VB.NET
History and Evolution • Visual Basic 1.0 for DOS was released in September 1992. The interface was textual, using extend ASCII characters to simulate the appearance of a GUI. • Visual Basic 2.0 was released in November 1992. The programming environment was easier to use, and its speed was improved.
History and Evolution • Visual Basic 3.0 was released in the summer of 1993 and came in Standard and Professional versions. • Visual Basic 4.0 (August 1995) was the first version that could create 32-bit as well as 16-bit Windows programs. It also introduced the ability to write non-GUI classes in Visual Basic.
History and Evolution • Visual Basic 5.0 (February 1997), Microsoft released Visual Basic exclusively for 32-bit versions of Windows. • Visual Basic 6.0 (Mid 1998) improved in a number of areas, including the ability to create web-based applications. • Visual Basic .NET (2002) (VB7) – Microsoft released VB.NET along with C# which received most of the attention
History and Evolution • Visual Basic .NET (2003) (VB 7.1)– Improvements were made in the performance and reliability of the .NET IDE • Visual Basic 2005 (VB 8.0) – Microsoft dropped the .NET portion of the title. Many improvements were made to reinforce Visual Basic .NET as a rapid application development platform and further differentiate it from C#.
History and Evolution • Visual Basic 2008 (VB 9.0) – released with the Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 on November 19, 2007. Release included: • True ternary operator If(boolean, value, value) to replace IIF function • Lambda expressions • XML Literals • Type Interface
Comparison to VBScript • Visual Basic is a Windows based programming language for individually running applications • VBScript is a scripting language mainly used to design web sites • Because of the way the purposes of these languages, Visual Basic can be written in an environment that aids in implementation whereas VBScript can only be written in a plain text file with no support
VB.NET Language Concepts • Uses Me instead of this • Does not use a ; for initialization • Used as a code behind for ASP.NET • Does not use standard escapes characters • Sub same as a function • Partial Classes
Bubble Sort Using VB Sub bubblesort(ByRef need(), max_min As Boolean) Dim now As Integer Dim never As Boolean Dim pick As Integer: pick = UBound(need) Dim lower As Integer: lower = LBound(need) For i = lower To pick For j = lower To pick – 1 If need(j) > need(j + 1) = Not max_min Then now = need(j): need(j) = need(j + 1): need(j + 1) = now never = True End If Next j If never = False Then Exit Sub Else never = False Next i End Sub
Verification of Data Example Private Sub Emp_Name_AfterUpdate() If Nz(DLookup("Emp_Name", "Employees", _ "Emp_Name='" & Me.Emp_Name & "'"), "zzzz") <> _ "zzzz" Then MsgBox & _ "That name already exists in the employee table.“ End Sub
Array Code Examples Dim strData() As String = {"Joe Hasterman", "Ted Mattison", "Joe Rummel", "Brian _ Gurnure", "Doug Landal"} Dim strMatrix(,) As String = {{"Red", "Green"}, {"Yellow", "Purple"}, {"Blue", "Orange"}} Dim strMatrix(6) As String strArray(0) = “Hello” strArray(1) = “Help” strArray(2) = “Hangover” strArray(3) = “Happened” strArray(4) = “Headache” strArray(5) = “Aspirin”