Fibre Distributed Data Interface
220 likes | 455 Vues
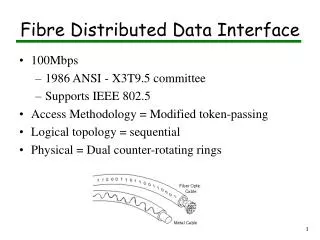
Fibre Distributed Data Interface. 100Mbps 1986 ANSI - X3T9.5 committee Supports IEEE 802.5 Access Methodology = Modified token-passing Logical topology = sequential Physical = Dual counter-rotating rings. Dual-Ring Topology. Subnets. Dual-Ring Topology. P rimary ring Traffic

Fibre Distributed Data Interface
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fibre Distributed Data Interface • 100Mbps • 1986 ANSI - X3T9.5 committee • Supports IEEE 802.5 • Access Methodology = Modified token-passing • Logical topology = sequential • Physical = Dual counter-rotating rings
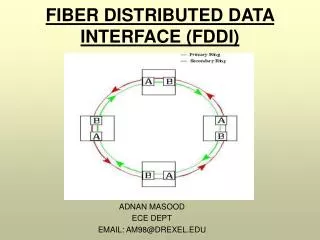
Dual-Ring Topology • Primary ring • Traffic • FDDI Reconfigures the network • Redundancy • Transmission • Cable Failure • Ring Failure • The total cable length of both rings combined must not exceed 200 km, and it cannot hold more than 1000 computers.
Topology • FDDI operates at 100 Mbps over a dual-ring topology that supports 500 computers over a distance of up to 100 km • More than one computer at a time can transmit • Capacities should be divided in half. • FDDI network should be limited to 500 computers and 100 km of cable.
FDDI (continued) A FDDI network
FDDI • Connects large and small minicomputers • Back-end networks • FDDI works with backbone networks to which other low-capacity LANs can connect • LANs that require high data rates • File transfer, Video, CAD & CAM
FDDI in Star • FDDI computers can accommodate point-to-point links to a hub.
Built-in reliability • High degree of reliability and security • EMI • RFI • Two Rings • Primary ring – data • Secondary ring – backup • Single Hub or connector • 500 nodes at 2km apart • SAS – single attachment station • DAS – dual attachment stations
Beaconing • With beaconing, the computer that detects a fault sends a signal, called a "beacon," onto the network. • The computer continues to send the beacon until it notices a beacon from its upstream neighbour, and then it stops sending.
Standards • Distances in FDDI LAN • Impractical to turn a free token to busy • Physically removes token and transmits an entire Data Frame. • Numerous messages can be sent • Synchronous Frames
Modified Token Passing • Transmits as many frames as it can produce within a predetermined. • There can be several frames circulating on the ring at once. • Higher throughput than a Token Ring network, which allows only one frame at a time to circulate.
Application of FDDI • Bandwidth drivers fall into two categories: • Network Architecture Trends • Network Application Trends • LANs = more and more users • FDDI networks form the backbone
Campus Backbone • Connecting LANs located throughout a series of closely situated buildings. • Ring circumference can equal 200 km • Multiple FDDI LANs • 100 Mbps FDDI building backbone • Connecting numerous 10-Mbps Ethernet • Servers connected via connectors
High-Bandwidth Workgroups • FDDI LANs connecting as few as 20 computers • High-bandwidth communication • CAD/CAM Workstations • Power Users • GUI
High-Bandwidth Subgroups • In some cases only 2 or 3 devices such as servers, require high-bandwidth. • Increased demand • Distributed Computing • Data Distribution