The Three Stages of Learning: Cognitive, Associative, and Autonomous
100 likes | 124 Vues
Learn about the three stages of learning, how teachers and coaches provide guidance at each stage, and the importance of understanding these stages when planning training activities. Explore the links between practice, motivation, feedback, age/experience, skill type, and individual learning.

The Three Stages of Learning: Cognitive, Associative, and Autonomous
E N D
Presentation Transcript
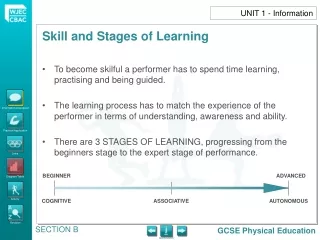
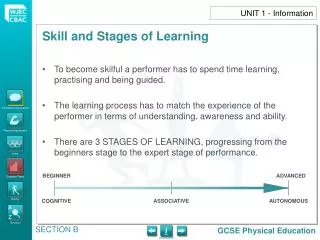
To become skilful a performer has to spend time learning, practising and being guided. The learning process has to match the experience of the performer in terms of understanding, awareness and ability. There are 3 STAGES OF LEARNING, progressing from the beginners stage to the expert stage of performance. UNIT 1 - Information BEGINNER ADVANCED COGNITIVE ASSOCIATIVE AUTONOMOUS
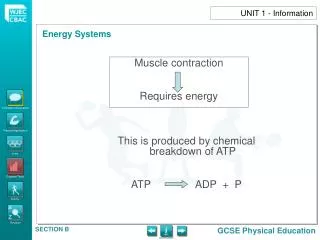
The age and experience of a person are contributing factors when deciding whether a skill is Basic or Complex e.g. catching or throwing a ball may be a basic skill for a teenager but a very complex skill for a young child. The process of LEARNING depends on the individual. Teaching/ Coaching – needs to match the development of each performer, otherwise the learning process is slowed down because of unreasonable demands and pressure. UNIT 1 - Information
COGNITIVE STAGE The beginners needs to understand what to do A clear mental picture of the activity is required A lot of time must be given to performing the technique Outcome isn’t so important at this time The beginners need to be shown and told what to do Clear demonstrations, simple and not overloaded instruction Many mistakes will occur, help would be needed to learn from the mistakes Praise is important in feedback UNIT 1 - Information
ASSOCIATIVE STAGE Techniques have been learnt Concentration on the skill Performance of the skill improves Fewer errors made Some ability to understand and correct the errors Better able to deal with more information and more complex information Both Internal and External Feedback used to improve performance UNIT 1 - Information
AUTONOMOUS STAGE Skills have become automatic Allows for more concentration on the outcome of the skill and to the tactical and strategic decisions of the activity Few errors, and they can be self-corrected Coaching only needed for the finer details of skill and tactics. Consistency is high, movement is smooth and fluent Intense practice needed UNIT 1 - Information
Classroom Using 3 videos to demonstrate each of the 3 stages of learning. Video of COGNITIVE STAGE to demonstrate: A clear and simple demonstration of a skill Attempts and errors by the beginners The beginners understanding what has to be done Video of ASSOCIATIVE STAGE to demonstrate: Ability to understand and correct errors Better ability to deal with more and more complex information Techniques have been learnt Video of AUTONOMOUS STAGE to demonstrate: Skills have become automatic Greater attention to tactics Few errors, and they can be corrected Consistency UNIT 1 – Practical Application
Classroom UNIT 1 – Practical Application
LEARNING CHARACTERISTICS OF A SKILLED PERFORMER/ PEFORMANCE GUIDANCE PRACTICE SKILL UNIT 1 - Links
Name and explain three stages of learning you go through when learning a skill. How would a teacher/ coach give guidance at each stage of learning? What is the link between PRACTICE and the stages of learning? Why is an understanding of the 3 stages of learning important for a teacher/ coach when planning training activities? UNIT 1 - Activity
UNIT 1 – Key Facts/ Glossary LEARNING TIME AGE / EXPERIENCE TEACHING INDIVIDUAL 3 STAGES COGNITIVE ASSOCIATEIVE AUTONOMOUS LINKS TO GUIDANCE PRACTICE MOTIVATION TYPE OF SKILL FEEDBACK