MARKET SEGMENTATION Chapter 7
531 likes | 1.11k Vues
MARKET SEGMENTATION Chapter 7. MBAADM5 roger bancilo. Chapter Overview:. What is Market Segmentation Levels of Market Segmentation Bases for Segmenting Markets. 3 Steps in Target Marketing (S T P). Segmentation Marketing Identify bases for segmenting the market Develop segment profiles

MARKET SEGMENTATION Chapter 7
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MARKET SEGMENTATIONChapter 7 MBAADM5 roger bancilo
Chapter Overview: • What is Market Segmentation • Levels of Market Segmentation • Bases for Segmenting Markets
3 Steps in Target Marketing(S T P) • Segmentation Marketing • Identify bases for segmenting the market • Develop segment profiles • Target Marketing • Develop measure of segment attractiveness • Select target segments • Market Positioning • Develop positioning for target segments • Develop a marketing mix for each segment
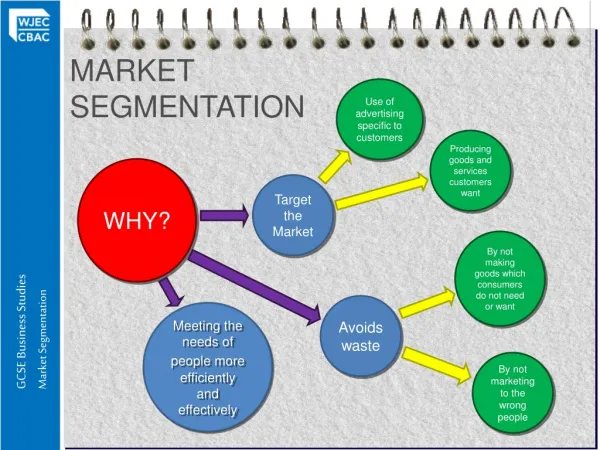
Market Segmentation • CONCEPT AND DEFINITION The concept of market segment is based on the fact that the market of commodities are not homogeneous but they are heterogeneous. Market represent a group of customer having common characteristics but two customer are never common in their nature, habits, hobbies, income and purchasing techniques.
Defining Market Segmentation • According to Philip Kotler , “Market segmentation is sub-dividing a market into distinct and homogeneous subgroups of customers, where any group can conceivably be selected as a target market to be met with distinct marketing mix.”
Market Segmentation • Market Segmentation is a method of “dividing a market (Large) into smaller groupings of consumers or organizations in which each segment has a common characteristic such as needs or behavior.”
Evolving Marketing Strategies • Mass Marketing: • The term mass market refers to a large, undifferentiated market of consumers with widely varied backgrounds. • Products and services needed by almost every member of society are suited for the mass market. Such items as electric and gas, utilities, soap, paper towels and gasoline, for example, can be advertised and sold to almost anyone, making them mass market goods.
1. Mass Marketing • An attempt to appeal to an entire market with one basic marketing strategy utilizing mass production, mass distribution and mass promotion of one product for all buyers. Also called undifferentiated marketing. • The appeal of mass marketing is in the potential for higher total profits. Companies that employ the system expect the larger profit to result from: • (1) expanded volume through lower prices, and • (2) reduced costs through economies of scale made possible by the increased volume. • Henry Ford applied the concept in the automobile industry. His Model-T was conceived and marketed as a "universal" car — one that would meet the needs of all buyers.
Mass Marketing Ford Model-T was the first to mass market automobiles. Ford mass produced by assembly line, mass distributed through dealers, and mass promoted one product for all buyers. Henry Ford epitomized this strategy when he offered the Model- T Ford in one color , black.
2.SEGMENT MARKETING A market segment consists of a large identifiable group of customers within a market who share a similar set of needs and wants, purchasing power, geographical location, buying attitudes, or buying habits. Identifiable Group with in a Market with Similar • Similar Needs & Wants • Purchasing Power • Geographical Location • Buying Attitudes
Example: Automakers may identify four broad segments in the car market. Buyers who are primarily seeking: 1. Low-cost Basic Transportation Toyota Wigo, Mitsubishi Mirage, Honda Brio, Kia Picanto, Hyundai Eon & i10, Tata Indigo
2.Driving Thrills & High Performance Toyota 86, Subaru BRZ, Subaru WRX STI, Ford Mustang, Chevrolet Camaro, Nissan GTR
3. Luxurious Driving Experience Lexus LFA, Mercedes, BMW, Audi, Bently, Meserati
4. Supercar / Hypercar McLaren, Ferrari, Bugatti, Lamborghini, Pagani, Renault
5. Car Safety Features Volvo Top Safety Features Volvo 360 Degrees Surround Camera; Blind Spot Information System, Lane Keeping Warning, Volvo Adaptive Cruising, Park Assist Pilot, Active High beam Headlights
Safety Features Subaru Forester Strong Utilitarian Body Structure, Eye Sight Camera Off-road Safety with X Mode , Best crash-test ratings in its class
Safety Features Ford Focus & Ford Explorer Ford Focus: Active City Stop, Blind Spot Warning, Self-parking Ford Explorer: Inflatable seatbelt
FLEXIBLEMARKETOFFERING • Consists of the product and service elements that all segment members value, plus options (additional charge) that some segment members value. • Even in segments, 100 % of their needs are not the same.
FLEXIBLEMARKETOFFERING • Consists of two parts. • Naked Solution : - products and services that all members of the segment values. • Discretionary options : - that some segment members value. Each option might carry an additional charge.
FLEXIBLEMARKETOFFERING • Need: Low Cost Basic Transportation • Naked Solution: Mitsubishi Mirage • Discretionary options: 2 Trims in 4 variants to choose from Mirage GLX (MT) – P503,000 Mirage GLX (CVT) – P553,000 ^P50K (CVT) Mirage GLS (MT) – P598,000 ^P95K (Trim) Mirage GLS (CVT) – P648,000 (MT) – Manual Transmission (CVT) – Continuous Variable Transmission (Automatic)
FLEXIBLEMARKETOFFERING Manual or CVT?
FLEXIBLEMARKETOFFERING Mirage GLS (MT) – P598K Mirage GLX (MT) - P503K • Ignition key starter • Key entry • Option: SAT-NAV system • Option: Touch screen multimedia entertainment • 2 Speakers • Non leather wrapped steering wheel • Manual control air con • Driver side airbag only • 14” steel rim w/ hubcaps • No fog lamps • No rear spoiler • 2 front doors power windows • Option: ABS w/EBD • Start/stop push button starter system • Keyless entry system • SAT-NAV equipped touch screen multimedia entertainment • 6 Speakers • Leather wrapped steering wheel • Automatic climate control air con • Twin airbags • 15” alloy wheel • Fog Lamps • Rear spoiler • Central locking 4 door power windows • ABS w/ electronic brace-force distribution
FLEXIBLEMARKETOFFERING Delta Airlines offers all economy passengers a seat and soft drinks. It charges economy passengers extra for alcoholic beverages.
2. NICHE MARKETING • Group of customers seeking a distinctive mix of benefits who are ready to pay extra premium. • A niche is a more narrowly defined customer group typically a small market whose needs are not being well served. Marketers usually identify niches by dividing a segment into sub segments or by defining a group seeking a distinctive mix of benefits. • Niche = segment sub – segments
NICHE MARKETING Ex. Car buyers who are primarily seeking for thrills and high performance. [MT] Manual Transmission [CVT] Continuous Variable Transmission with Paddle shifter
3. LOCAL MARKETING • Marketing programs tailored to the needs & wants of local customer groups in trading areas, neighborhoods , etc. • This trend is called grass roots marketing.
4. INDIVIDUAL MARKETING • Ultimate segmentation – segments of 1 or customized marketing or one-to-one marketing. • Customerization – empower the consumers to design the product or service offering of their choice.
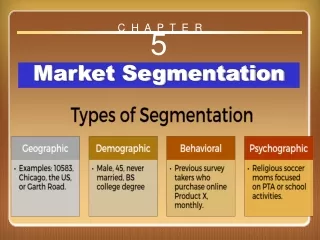
GEOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION Divides the market into different geographical units such as nations, regions, states, counties, or cities. Mcdonalds globally, sell burgers aimed at local markets, for example, burgers are made from lamb in India rather then beef because of religious issues. In Mexico more chilli sauce is added and so on. Tereyaki burger in Japan. Toyota Motor Corporation
DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION Demographic segmentation is the most popular segmentation method because consumer needs, wants, and usage often vary closely with demographic variables and are easier to measure than other types of variables.
Age Demographic Segmentation Income Level Family Ethnicity Education Dr. Rosenbloom
Age and life-cycle stagesegmentation is the process of offering different products or using different marketing approaches for different age and life-cycle groups. As people age their needs and wants change, some organizations develop specific products aimed at particular age groups for example nappies for babies, toys for children, clothes for teenagers and so on. Gender segmentation is commonly used within the cosmetics, clothing and magazine industry. Income segmentation is another strategy used by many organizations. Products and services are also aimed at different lifecycle segments. Holidays are developed for families, the 18-30's singles, and for those in their 50's.
Psychographic Segmentation Psychographic segmentation divides buyers into different groups based on social class, lifestyle, or personality traits.
Behavioral Segmentation Behavioral segmentation divides buyers into groups based on their knowledge, attitudes, uses, or responses to a product • Occasion • Benefits sought • User status • Usage rate • Loyalty status
Behavioral Segmentation Occasionsegmentation divides buyers into groups according to occasions when they get the idea to buy, actually make purchases, or respond to a product. Benefitsegmentation requires finding the major benefits people look for in the product class, the kinds of people who look for each benefit, and the major brands that deliver each benefit.
Behavioral Segmentation User status divides buyers into ex-users, potential users, first-time users, and regular users of a product. Usage rate divides buyers into light, medium, and heavy product users. Loyalty status divides buyers into groups according to their degree of loyalty
Segmentation Criteria[MASDA] To be useful, a market segment must be: • Measurable • Accessible • Substantial • Differentiable • Actionable Requirements for Effective Segmentation
Segmentation Criteria Measurable examples include the size, purchasing power, and profiles of the segments. Accessiblerefers to the fact that the market can be effectively reached and served. Substantial refers to the fact that the markets are large and profitable enough to serve. Differentiable refers to the fact that the markets are conceptually distinguishable and respond differently to marketing mix elements and programs. Actionable refers to the fact that effective programs can be designed for attracting and serving the segments.