What is a Protist ?
450 likes | 1.17k Vues
What is a Protist ?. How are Protists related to other eukaryotes? . Does everyone agree how to classify protists?. No, at present, biologists do not agree how to classify protists

What is a Protist ?
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is a Protist? How are Protists related to other eukaryotes?
Does everyone agree how to classify protists? • No, at present, biologists do not agree how to classify protists • The amount of diversity among the protists, is much greater than within or between the other three eukaryotic kingdoms
The Protist Dilemma • Protists are grouped together solely because they are not fungi, plants or animals • Furthermore, many protists are more closely related to members of other eukaryotic kingdoms than they are to other protists.
Current Protist classification • It has been proposed that the protista kingdom be divided into six groups or clades • Today, while we still use the term Protist, this is not a single kingdom, but a collection of organisms in six clades
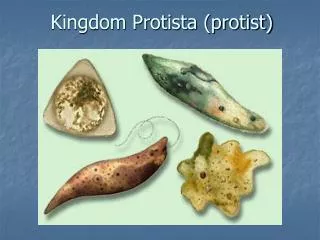
What is a Protist? • A protist is a eukaryote (has a nucleus) • A protist is any eukaryote that is not a plant, animal or fungus
Are all protists unicellular? • No, although most are unicellular, some protists are colonial, and some like the giant kelp are multicellular. Unicellular Colonial Multicellular
How do Protists Move? Some move with flagella • Long whip-like projections • One to two per cell • Examples • Trypanosoma • Euglena Trypanosoma
Euglena • Two flagella • No cell wall • Chloroplasts
How do Protists move? • Some move with cilia • Cilia can be used for feeding and movement • Cilia are short and used like oars on a boat • Example • Paramecium
Trichocysts Oral groove Lysosomes Gullet Anal pore Contractile vacuole Micronucleus Macronucleus Food vacuoles Cilia Ciliates - Paramecium Go to Section:
Some do not move • Those that do not move produce spores and live as parasites • Plasmodium causes malaria • Cryptosporidium spreads through contaminated drinking water and caused intestinal disease
Excavates: feeding groove, flagella • Diplomonads • Giardia is an intestinal parasite that causes cramping and diarrhea • Discicristates • Euglena is free living and can use its chloroplast for photosynthesis or can live as a heterotroph • Trypansoma causes African sleeping sickness; carried by tsetse flies
Euglena Chloroplast Carbohydrate storage bodies Gullet Pellicle Contractile vacuole Nucleus Flagella Eyespot Go to Section:
Chromalveolates: very diverse group; most are photosynthetic • Phaeophytes = multicellular brown algae • Chrysophytes = unicellular golden algae • Diatoms = unicellular algae with intricate silicon dioxide (silica) shells • Ciliates = paramecium are not photosynthetic • Dinoflagellates = half are photosynthetic, half are heterotrophs; some are luminescent • Apicomplexans = parasitic Plasmodium
Brown algae Phaeophytes • Photosynthetic • Chlorophylls a and c • Brown accessory pigment fucoxanthin • Multicellular • Giant kelp, Fucus
Photosynthetic protists • Chrysophytes • “Golden plants” • Gold-colored chloroplasts • Cell walls contain pectin instead of cellulose • Store food as oil rather than starch • Can form thread like colonies
Photosynthetic protists Diatoms • Glass like cell walls • Cell walls contain silicon (Si) • Cell walls like petri dish
Photosynthetic protists Dinoflagellates • Luminescent • “Fire plants” • Half photosynthetic • Half heterotrophs • Two flagella
Apicomplexan • Plasmodium • Mosquito borne parasites like the species that causes malaria
Cercozoa, Foraminiferan, Radiolarian • Have pseudopods • Many produce protective shells Foraminiferans Heliozoan
Rhodophytes Red Algae • Chlorophyll a • Red accessory pigment – phycobilin • Absorbs blue light • Grows very deep • Multicellular • Nori
Ecology of photosynthetic protists • Base of the food chain • Half of the photosynthesis on earth is carried out by phytoplankton
Ecology of photosynthetic protists • Algal blooms • Caused by too much pollution or nutrients • Deplete water of oxygen • Kill fish and invertebrates • Dinoflagellates cause “red tides” • Red tides produce toxins which can be taken in by shellfish. Eating these shellfish can cause illness, paralysis and death
Green algae • Phylum Chlorophyta • Same chlorophyll and cell wall composition as green plants • Chlorophyll a and b • Store food as starch • Found in fresh and salt water and on land • Unicellular, colonial and multicellular • Now classified with plants
Unicellular green algae • Chlamydomonas • Lives in ponds, ditches and wet soil • Egg shaped • Two flagella • Large, cup-shaped chloroplast
Colonial green algae • Spirogyra • Filamentous • Forms threadlike colonies • Spiral chloroplasts • Volvox • Hollow spheres • 500 – 50,000 identical cells • Some cell specialization
Human uses of algae • Oxygen • Food (nori; thickening agent (carrageenan) in ice cream, egg nog, chocolate, salad dressing) • Industry (plastics, waxes, paints, lubricants) • Science labs (agar)
Alternation of generation – alternating between diploid and haploid organisms • Diploid – having two copies of each chromosome • Haploid – having one copy of each chromosome • Gametophyte – haploid gamete producing organism • Sporophyte – diploid spore producing organism
Heterotrophic protists • Amoebozoa = Amoebas use pseudopods for movement and feeding • Ciliates = Paramecia use cilia to move food to gullet; food vacuoles and lysosomes digest the food; waste is released through the anal pore • Slime Molds and Water Molds absorb food through their cell walls from dead or decaying matter; decomposers
Contractile vacuole Pseudopods Nucleus Food vacuole Section 20-2 An Amoeba Go to Section:
Water molds • Cells are multinucleate • Cell walls of cellulose • White fuzz on dead fish in water • Plant parasites on land Cause potato blight responsible for potato famine
Reproduction in water molds • Can produce sexually and asexually • Motile (swimming) spores • Antheridium produces sperm • Oogonium produces eggs
Mutualistic relationships • Zooxanthellae – live inside coral and provide food through photosynthesis • Trychonympha –live in the gut of termites and digest cellulose