Understanding Finite Charges: Polarizability Examples in Physics
70 likes | 179 Vues
Explore what happens when charge q is finite through examples q2 > q1 > 0. Learn about inducing charge p1 at point P and finding polarizability α. Dive into techniques like neutralizing metal ball and tape, charging by induction, and mathematical tools like Trig Functions, Derivatives, Integration, and Change of Variable.

Understanding Finite Charges: Polarizability Examples in Physics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
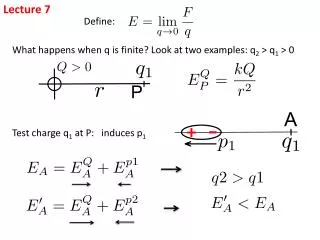
Lecture 7 Define: What happens when q is finite? Look at two examples: q2 > q1 > 0 Test charge q1 at P: induces p1
Example Polarizability Find q, α Assume origin at the pipe:
“Neutralize” the metal ball “Neutralize” the tape
Review Math 1. Trig Functions: 2. Derivatives: 3. Integration:
Review Math continued... , Put together: Uniform Charge -- or
Preview Analytic Result Change of Variable in Integration: Math ID: (pg 633)