Group Accounting and Subsidiary Undertakings Overview
90 likes | 202 Vues
Understand the changes in technology, business structuring, and group accounting. Learn about FRS 2 for subsidiary undertakings, dominant influence, exemptions, and exclusions. Get insights on preparing consolidated accounts and managing associate entities.

Group Accounting and Subsidiary Undertakings Overview
E N D
Presentation Transcript
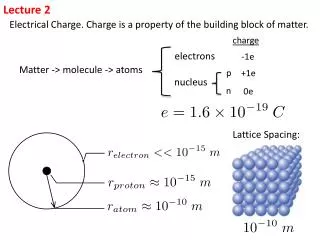
AC303 lecture 2 • Changes in technology, financing, business structuring and diversification • practice of accounting for single business enterprises became inappropriate • group accounting required to preserve true and fair view because of inter-connected companies and complex relationships • Made clear by legislation and regulation that group comprises parent, subsidiaries, associates and significant joint ventures
FRS 2 - Accounting for subsidiary undertakings • Parent/subsidiary relationship exists if any of the following apply (Para 14): • Parent holds a majority of the voting rights • Parent is a member of the undertaking and has the right to appoint or remove directors holding a majority of the voting rights at meetings of the Board on all, or substantially all, matters • Parent has the right to exercise dominant influence (influence to control operating and financial policies, notwithstanding rights or influences of other parties)
FRS 2 - Accounting for subsidiary undertakings • Examples of dominant influence • provisions contained in memorandum or articles of association • control contract authorised by memorandum or articles of association • Parent is a member of the undertaking and controls it alone pursuant to agreement with other shareholders • Parent has a participating influence and (i) actually exercises dominant influence or (ii) both are managed on a unified basis • Parent of a subsidiary is also the parent of any sub-subsidiaries • A participating influence is an interest held on a long term basis with a view to securing a contribution to its own activities. Twenty percent or more is presumed to be a participating influence.
Group accounts • Parent/subsidiary relationship is not only based on percentage ownership • Company A owns 20% of company B. Majority board representation and controls all decisions. Is company B a subsidiary of company A? • All parents must prepare group accounts, subject to exemptions and exclusions
Exemptions • Group is classified as ‘small’. Two of following criteria must be met for two successive years: • balance sheet total< IR£6 million • annual turnover<IR£12 million • average number of employees<250 • Parent undertaking is not a company limited by shares or by guarantee • Above exemption does not apply to banks, insurance companies or public limited companies • Intermediate parent undertaking • Irish parent it itself a 90% or greater subsidiary of an undertaking established under EU law and any minority have approved an exemption for Irish company from preparing group accounts
Excluding subsidiaries • FRS2 requires exclusion of subsidiaries in following circumstances: • severe long term restrictions substantially hinder the rights of the parent to the assets or management of the company • interest in the subsidiary is held exclusively for resale and has not previously been consolidated • activities of the subsidiary are so different from those of other undertakings to be included in the consolidation that to consolidate would be incompatible with the obligation to present a true and fair view • FRS2 does not allow exclusion on the basis of undue expense or delay required to acquire the information
Examples • T plc has two subsidiaries, one of which, R Limited has a 90% subsidiary. T plc is itself a subsidiary of D GmbH. Is T plc required to prepare consolidated accounts? • A plc has one 100% subsidiary, P Limited, for the last three years. In December 2001, A plc decides to sell P Limited. There are interested buyers but, by March 2002, the sale is still outstanding. The directors believe this is temporary and fully expect the sale to go through in April. Should P Limited be included in the 2001 year end consolidated accounts?
Example • Swift plc has investments in F Ltd (50%), M Ltd (65%) and Slow Ltd (90%). Swift plc holds a majority of the voting equity in F Ltd and M Ltd and has changed the composition of those Boards since they were acquired. It only has 40% of the voting equity in Slow Ltd and failed in any attempts to change the composition of the Board. How should Slow Ltd be treated for consolidation purposes?
Associate definition - FRS 9 • An associate is an undertaking in which another undertaking has a ‘participating interest’ and • over which that other undertaking has significant influence and • is not controlled by that other undertaking either solely or jointly • No minimum shareholding necessarily indicative of significant influence but 20% is the rebuttable presumption • Active involvement and influence in the strategic issues of an entity would indicate significant influence