Introduction to Arrays: Understanding Declaration, Initialization, and Usage in Java
120 likes | 256 Vues
This chapter provides a comprehensive introduction to arrays in Java. Arrays are ordered collections that store multiple elements of the same type, indexed starting at 0. Learn how to declare and instantiate arrays using the `new` keyword, and explore methods for assigning values and iterating through arrays with loops. Understand the difference between passing intrinsic types by value and objects by reference, including how to handle arrays when passing them to methods. This guide also covers polymorphism and holding objects of a common type in an array for practical programming applications.

Introduction to Arrays: Understanding Declaration, Initialization, and Usage in Java
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 10 Introduction to Arrays
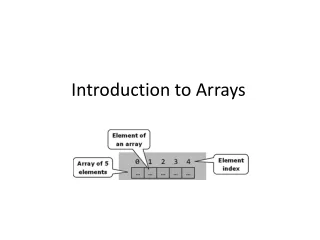
What is an array? • An array is an ordered collection that stores many elements of the same type within one variable name. • Elements are the items in an array. • Each element is identified with an index number. • Index numbers always start at 0 for the first element.
Declaring Arrays • Identify type of array • Use square brackets • int[] myArray; • Declares an array of int values
Instantiating Arrays • Use the new keyword • Identify number of elements • myArray = new int[1000]; • Instantiates myArray with 1000 elements • You can declare and instantiate in one line • int[] myArray = new int[1000];
Putting Values in the Array • Use the index operator to assign a value at a particular place in the array. • myArray[10] = 100; • Assigns the value 100 to the 10th element in the array • Most programs use a for loop to iterate the array.
Initializing the Array • You can initialize the array with values at the same time the array is created. • int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Determining the Length of the Array • Use the length property to find the number of elements in the array. • System.out.println(myArray.length); • Displays the length of the array in the console • For ( int i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++ ); • Uses the length property to set up the for loop
Passing by Value • Intrinsic types are passed to methods by value. • A copy of the value is passed. • The original value is unchanged.
Passing by Reference • Objects are passed to methods by reference. • The reference points to the original object. • A change to the object affects the object in the calling method.
Passing Arrays to Methods • An array is an object type. • Passed by reference • Elements of arrays are not necessarily passed by reference. • Depends on the underlying element type • Extracting int elements from an array and passing them to a method passes them by value
Using Polymorphic Objectsin an Array • An array can hold objects that: • Derive from the same base class • Implement a common interface