Complex Patterns of Heredity
160 likes | 395 Vues
Complex Patterns of Heredity. Advanced Biology DNHS. Complex Inheritance Patterns. Sometimes the laws and principles of genetics established by Gregor Mendel do not always explain the inheritance patterns seen in an organism. Incomplete Dominance.

Complex Patterns of Heredity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Complex Patterns of Heredity Advanced Biology DNHS
Complex Inheritance Patterns • Sometimes the laws and principles of genetics established by Gregor Mendel do not always explain the inheritance patterns seen in an organism.
Incomplete Dominance • The heterozygous or hybrid individual will show an intermediate phenotype between the two homozygous individuals • Example – Snap Dragons flower color red crossed with white = pink
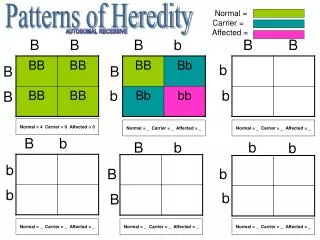
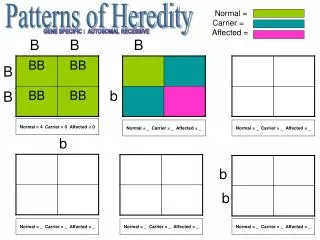
R = red R’ = white R R R R’ RR’ RR R’ RR’ R RR’ R’ RR’ R’R’ RR’ RR’ R’ Genotype: All RR’ hybrid Genotype: ¼ RR; ½ RR’; ¼ R’R’ Phenotype: All pink Phenotype: ¼ red; ½ pink; ¼ white
Codominance • The heterozygous individual will show the phenotypes of each of the homozygous individuals • Example – chickens, black+white=checkered (black and white)
Multiple Alleles • Situation wherein there exists more than two alleles for a specific trait. • Example – Blood type in humans (A, B, O alleles)
Sex Linked Traits • When a trait is seen in one sex more often than another due to a gene that is carried on one of the sex chromosomes • Examples – eye color in fruit flies and hemophilia and color blindness in humans
Polygenic Inheritance • When a trait is influenced by many genes • Tends to be a wide range of phenotypic variation • Examples: skin color, hair color, height in humans
Test Crosses • A situation in which there is an individual of unknown genotype • To determine the genotype you would cross it with a pure recessive individual
Pedigree • A graphic genetic family tree that follows a trait through several generations
Aneuploidy • A condition of having an abnormal chromosome number • Example – Down’s Syndrome, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies (Turner Syndrome)