Ch 9
160 likes | 321 Vues
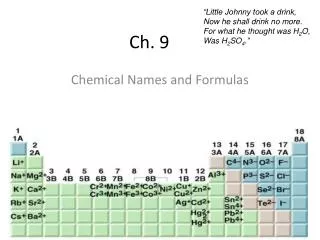
Ch 9 . Highlights – Ch 9. Important vocab : laissez-faire Neutral rights Impressment War Hawks nationalism Important concepts: Marbury v. Madison and Judicial Review Louisiana Purchase 1803 Lewis and Clark Expedition Pikes Expedition Embargo Act

Ch 9
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Highlights – Ch 9 Important vocab: • laissez-faire • Neutral rights • Impressment • War Hawks • nationalism Important concepts: • Marbury v. Madison and Judicial Review • Louisiana Purchase 1803 • Lewis and Clark Expedition • Pikes Expedition • Embargo Act • War of 1812 & Treaty of Ghent (James Madison now president)
Thomas Jefferson • Jefferson is a republican • Republicans/Jefferson believed in laissez-faire • Laissez-faire = French philosophy which means “let people do as they choose”. • Jefferson believed in reducing the power and size of the federal government. Let people do as they choose.
Marbury v. Madison • John Marshall is Chief Justice of Supreme Court when this case was heard • Q: What principal did Marbury v. Madison establish? • A: Judicial Review • Q: Define Judicial Review • A: Supreme Court has the power to review the other two branches and determine if their actions agree with the constitution.
Louisiana Purchase • U.S. (Jefferson president) purchased Louisiana Territory from France/Napoleon in 1803. • Paid $15 million dollars. • Doubled the size of the United States • (Probably the best land purchase the U.S. has ever made)
Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the United States!!!! Lou. Purchase 1803 US 1800 Claimed by Spanish
Lewis and Clark (map page 284) • United States wanted to explore the new Louisiana Territory • L & C hired to travel along Missouri River and into Oregon Country • Jefferson sends Lewis and Clark to collect data on people (Native Americans), plants, animals, and geography of the land west of Mississippi River. • Sacagawea (famous Native American guide)
Pike’s Expedition • Jefferson sent Zebulon Pike on two expeditions, traveling through the upper Mississippi River valley and into region we now call Colorado • In Colorado, he found Pikes Peak
Foreign policy • GB and Fr went to war in 1803. • A nation not involved in a conflict had “neutral rights” = meaning the right to sail the seas and not take sides. • So US goal is to remain neutral and trade with both sides • 1805 GB and Fr began violating our neutral rights. • Br needed sailors and began impressment= practice of forcing people to serve in the Br navy
Embargo Act • Embargo = prohibits trade with another country. • GB practice of impressment and it violation of America’s neutral rights led Jefferson to ban some trade with GB. • Then the British attack on the Chesapeake (US ship) further angered US and led to the passage of the Embargo Act. • Embargo Act banned imports and exports with ALL foreign countries. (Jefferson wanted to prevent Americans from using other countries as go betweens)
Consequences of Embargo Act • US goal in passing Embargo Act was to prevent war with GB. • Not only is act not successful (as War of 1812 will occur), but also… • Embargo Act was a disaster as it wiped out all American commerce (trade) with other nations. • GB just continued to trade with the rest of the world
War of 1812 • War Hawks – group of young republicans in Congress that pressured the president to declare war against Britain. • John C Calhoun and Henry Clay were both war hawks • Spring of 1812 – Madison declares war on GB • Often referred to as either “Madison’s war” or “2nd fight for Independence”
Native American Role in War of 1812 (Native Americans – sided with British to fight their common enemy - the United States.) Tecumseh - Shawnee chief that built a confederacy among Native Americans • Goal – stop white expansion West • Killed in War of 1812 and with him dies the hope of preventing westward expansion of the white man
The Prophet (brother to Tecumseh) • Urged Native Americans to return to their own customs/traditions. (Ex -- give up white man dress, drinking, etc.) End of War of 1812 – results in end of alliance with GB and downfall of Nat Americans in U.S. (Jackson will become president in 1828 and will move Nat Americans to Indian Territory.)
Treaty of Ghent • War ends with Treaty of Ghent – simply a truce. No change in borders. No mention of impressment. Neutral rights became a dead issue with defeat of Napoleon • Before news of treaty reached battlefields, one final, ferocious, battle – Battle of New Orleans • Battle of New Orleans – Decisive battle for U.S. Andrew Jackson lead US military in this battle. Jackson became famous and helps him win presidency in 1828.