WWW and Internet
180 likes | 441 Vues
WWW and Internet. The Internet Creation of the Web Languages for document description Active web pages. Internet. ARPANET – 1970s. Protocols TCP/IP: Transmission Control Program/Internet Protocol - low level Telnet SMTP - Simple Mail Transport Protocol FTP - File Transfer Protocol.

WWW and Internet
E N D
Presentation Transcript
WWW and Internet • The Internet • Creation of the Web • Languages for document description • Active web pages
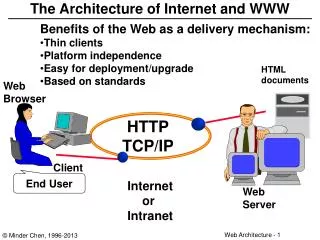
Internet • ARPANET – 1970s. • Protocols • TCP/IP: Transmission Control Program/Internet Protocol - low level • Telnet • SMTP - Simple Mail Transport Protocol • FTP - File Transfer Protocol
Creation of the Web WWW provides a semantic description of the information accessible through the Internet. Server program: to provide the document Client program: to read and display the document. Server and client communicate via HTTP - HyperText Transport Protocol.
Basic Idea WWW is based on the concept of a semantic description language. The power of the system is that the displayed document contains pointers to other documents called hypertext.
URL: Uniform Resource Locator Client program: uses URLs to locate documents and display in the web browser A database of addresses and names is maintained by a Domain Name Server.
Other programs Search engines – allow user to query site for desired information Web crawlers – crawler trace all links on a Web page to find other Web pages
Languages for documentdescription SGML: Standard Generalized Markup Language HTML – HyperText Markup Language XML – Extensible Markup Language
SGML SGML uses descriptive tags. DTD –document type declaration, describes the elements What is described: - Document presentation (e.g. boldface, italics) - Document structure (text split into divisions, chapters, paragraphs, etc) - Document history (author, revisions, etc)
HTML • HTML creates a virtual machine that web browsers are programmed to execute. • Important elements- • Sections – Separate parts of a document • Presentation – How documents look. • List – Lists of items • URLs – links to other web pages • Image URLs – displays pictures
XML An instance of SGML. Incorporates many features of HTML. Uses DTD to describe the semantics of the document.
Active web pages • Forms and CGI scripts • Java Applets
Forms and CGI scripts • Forms – Method to pass information between Web browsers and Web servers. • Information is entered by the user and then passed for processing to a program on the server system • CGI (Common Gateway Interface) scripts - programs that process the information
HTML forms <form method=“type” action= “location of cgi script to execute”> text </form> Perl is often used as language for such scripts
Java Applets Issue: Overloaded server Solution: Do more processing on client side of web JAVA APPLETS
Java applets • Run on the client machine • Java programs compiled into a machine independent code – bytecode for JavaVirtual machine. • Browsers on local systems have Java Virtual machine interpreter
Java Applet Example import java.awt.*; /* applet library */ public class hello extends java.applet.Applet public void paint(Graphics x) {x.drawString(“Hello World”, 100, 100);} Displayed by: <html><body> <applet code = “hello.class” width=200 height=200> </applet> </body></html>