Wire Propagation Effects
120 likes | 219 Vues
Learn about signal distortion, attenuation, and noise in wire propagation. Discover the impact of interference and tips for maintaining signal strength. Overcome practical issues like crosstalk and distance limits.

Wire Propagation Effects
E N D
Presentation Transcript
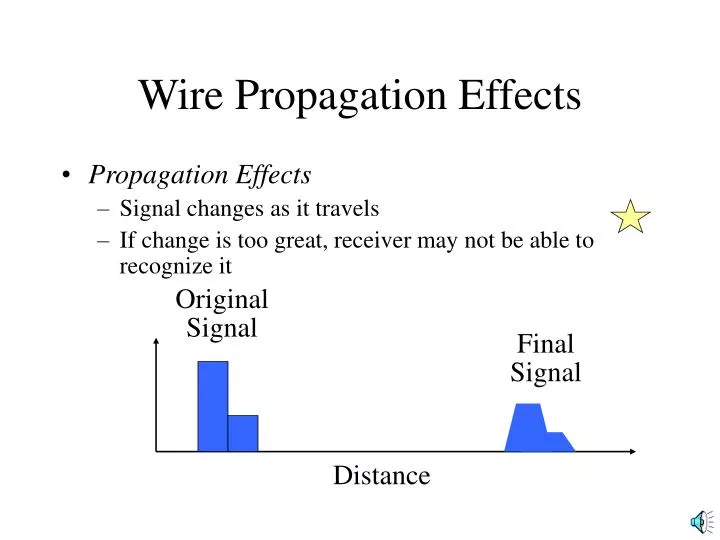
Wire Propagation Effects • Propagation Effects • Signal changes as it travels • If change is too great, receiver may not be able to recognize it Original Signal Final Signal Distance
Wire Propagation Effects: Attenuation • Attenuation: Signal Gets Weaker as it Propagates • May become too weak for receiver to recognize Signal Strength Distance
Wire Propagation Effects: Distortion • Distortion: Signal changes shape as it propagates • Adjacent bits may overlap • May make recognition impossible for receiver Distance
Wire Propagation Effects: Noise • Noise: Thermal Energy in Wire Adds to Signal • Noise floor is average noise energy • Random energy, so noise spikes sometimes occur Spike Signal Signal Strength Error Noise Noise Floor Time
Wire Propagation Effects • Noise and Attenuation • As signal attenuates, gets closer to noise floor • So noise errors increase with distance, even if the average noise level is constant Signal Strength Signal Noise Floor Distance
Wire Propagation Effects: SNR • Want a high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) • Signal strength divided by average noise strength • As SNR falls, errors increase Signal Strength Signal SNR Noise Floor Distance
Wire Propagation Effects: Noise & Speed • Noise and Speed • As speed increases, each bit is briefer • Noise fluctuations do not average out as much • So noise errors increase as speed increases OK Error One Bit One Bit Noise Spike Noise Spike Low Speed (Long Duration) High Speed (Short Duration) Average Noise During Bit Average Noise During Bit
Wire Propagation Effects: Interference • Interference • Energy from outside the wire (nearby motors, other wires, etc.) • Adds to signal, like noise • Often intermittent (comes and goes), so hard to diagnose Signal Signal Strength Interference Time
Wire Propagation Effects: Cross-Talk Interference • Cross-Talk Interference • Often, multiple wires in a bundle • Each radiates some of its signal • Causes “cross-talk” interference in nearby wires
Wire Propagation Effects:Cross Talk • Wire Usually is Twisted • Usually, several twists per inch • Interference adds to signal over half twist, subtracts over other half • Roughly cancels out • Simple but effective - + Interference Signal Single Twist
Wire Propagation Effects:Cross Talk • Terminal Cross-Talk Interference • Wire must be untwisted at ends to fit into connectors • So cross-talk interference is high at termination • Problems severe if untwist more than about 1.25 cm (1/2 inch) • Usually the biggest propagation effect Terminal Cross Talk
Practical Issues in Propagation Effects • Distance limits in standards prevent serious propagation effects • For instance, usually 100 meters maximum for ordinary copper wire • If stay within limits, usually no serious problems • Problems usually occur at connectors • Crossed wires • Poor connections • Cross-talk interference New