Happy Monday!
110 likes | 407 Vues
Happy Monday!. CO : I will understand and identify the structure and function of a carbohydrate. LO : I will write notes and build a carbohydrate. Notes: Biomolecules. Biomolecules are the molecules found in all living things. Biomolecules are organic compounds.

Happy Monday!
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CO: I will understand and identify the structure and function of a carbohydrate.LO: I will write notes and build a carbohydrate.
Notes: Biomolecules • Biomolecules are the molecules found in all living things. • Biomolecules are organic compounds. • Organic compound contain the element carbon (C) • All living things contain carbon • A substance without carbon is called inorganic Elements to know: C = carbon N = nitrogen H = hydrogen P = phosphorus O = oxygen
Structure: Functions: • Main source of immediate energy • Circle or ring shaped • Create a 1:2:1 ratio Elements: Good to know: • Often known as simple (monomers) and complex (polymers) • C, H, O Carbohydrate Monomer: Polymer: • Polysaccharide • Examples: starch, cellulose • Monosaccharide • Examples: glucose, sucrose
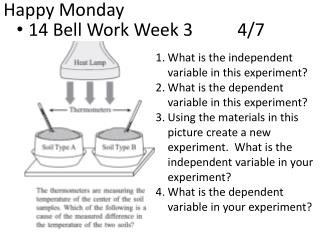
Making a Carbohydrate: • What monomer did you build? • What elements are present in your monomer? • How does the structure of your monomer allow it to complete its function?
Bellwork: • Which of the following is/are not carbohydrates? • C6H12O6 • C12H2406 • C6O12H6 • C6H12O14 • C12H24012
CO: I will understand and identify the structure and function of a lipid. I will compare it to a carbohydrate.LO: I will write notes and build a lipid. I will create a Venn Diagram to compare carbohydrates and lipids.
Structure: Functions: • Source for long term energy • Primary component of the cell membrane (hydrophobic) • Chain shaped • A backbone and 3 tails Good to know: Elements: • Saturated fats: contain single bonds • Unsaturated fats: contain double bonds • C, H, O Lipids Monomer: Polymer: • Triglyceride (lipid) • Fatty acids
Making a Lipid: • What kind of lipid did you make, saturated or unsaturated? How do you know? • What elements are in the lipids? • The glycerol in a lipid is often referred to as the glycerol backbone. Why do you think that is? 4. How does the structure of a lipid determine its function?
Bellwork • Examine the following pictures of steroids. What kind of biomolecule do you think they are? Why?
Bellwork • Be able to explain the joke