Understanding the Ideal Gas Law: Relationships Between Pressure, Volume, Temperature, and Moles
30 likes | 171 Vues
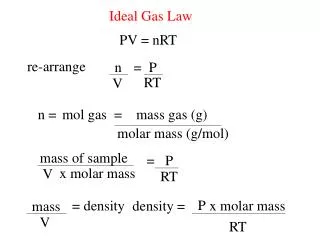
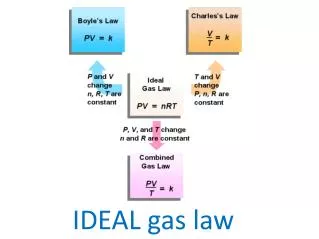
The Ideal Gas Law, expressed as PV = nRT, describes the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and the number of moles (n) of a gas. In this equation, R represents the universal gas constant, which varies depending on the units of measurement: 8.31 L·kPa/(K·mol), 62.4 L·Torr/(K·mol), or 0.0821 L·atm/(K·mol). Understanding how these variables interact helps predict gas behavior under various conditions, highlighting the importance of temperature in Kelvin and the significance of the number of moles.

Understanding the Ideal Gas Law: Relationships Between Pressure, Volume, Temperature, and Moles
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ideal Gas Law How are pressure, temperature, volume, and the number of moles related???
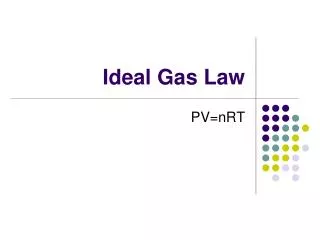
Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT Where… P = Pressure V = Volume IN LITERS n = Number of moles of gas R = Universal gas constant T = Temperature in Kelvin
Universal Gas Constant If the pressure is in… Kpa Then R = 8.31 LKpaKmol Torr Then R = 62.4 LTorrKmol Atm Then R = 0.0821 LatmKmol