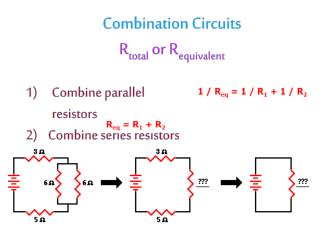
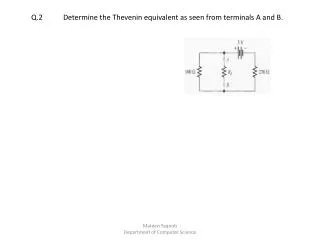
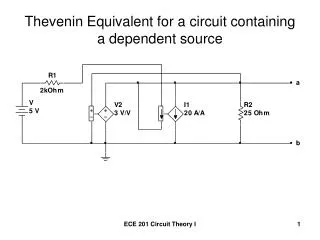
Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits
350 likes | 903 Vues
Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits. http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_1/chpt_10/8.html.

Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_1/chpt_10/8.html
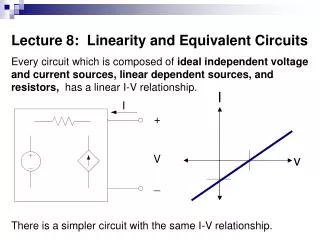
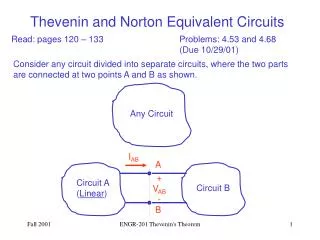
Thevenin's Theorem states that it is possible to simplify any linear circuit, no matter how complex, to an equivalent circuit with just a single voltage source and series resistance connected to a load.
To create the Thevenin Equivalent Circuit we need: • Value of the Thevenin Voltage Source • Value of the Thevenin Resistance
Determination of the Thevenin Voltage EThevenin = Open circuit voltage with load removed
Determination of the Thevenin Voltage EThevenin = Open circuit voltage with load removed EThevenin = 11.2
Determination of the Thevenin Resistance RThevenin = Net resistance in network with sources set to zero RThevenin = 0.8 ohms
Determination of the Thevenin Resistance (Alternative) RThevenin = EThevenin / IShort Circuit
Thevenin Theorem Summary EThevenin = 11.2 volts RThevenin = 0.8 ohms
The Maximum Power Transfer Theorem simply states, the maximum amount of power will be dissipated by a load resistance when that load resistance is equal to the Thevenin/Norton resistance of the network supplying the power.