Understanding Atomic Properties: Radius, Ionization Energy, and Electronegativity Patterns
90 likes | 216 Vues
This review explores key periodic trends in atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. We explain how atomic radius increases down a group and decreases across a period. Ionization energy trends show that ionization energy decreases down groups and increases across periods. Electronegativity follows similar trends, decreasing down groups and increasing across periods. We also pose questions about the smallest and largest elements, as well as those with the highest and lowest ionization energy and electronegativity, allowing for a deeper understanding of elemental behavior.

Understanding Atomic Properties: Radius, Ionization Energy, and Electronegativity Patterns
E N D
Presentation Transcript
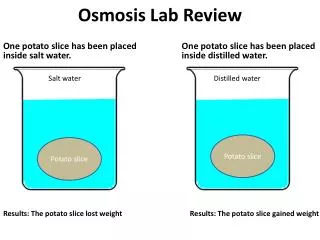
Lab Review It’s in the Cards Straw Lab
Atomic radius • Increases down a group • more energy levels • Decreases across a period • increasing attraction by additional proton-electron pairs
Ionization Energy • Decreases down groups • valence electrons further away from protons • Increases across periods • valence electrons closer to protons
Electronegativity • Decreases down groups • shared electrons are further from pull of protons • Increases across periods • same principal energy level, but more protons
Periodicity • has a pattern • repetition of the pattern • on the periodic table, row after row follows a similar pattern in its properties
Atomic radius • Which is smallest? • lithium • potassium • rubidium • Which is largest? • boron • nitrogen • fluorine
Ionization energy • Which has the lowest ionization energy? • magnesium • calcium • strontium • Which has the highest ionization energy? • aluminum • phosphorus • chlorine
Electronegativity • Which has the lowest electronegativity? • aluminum • gallium • indium • Which has the highest electronegativity? • calcium • germanium • bromine
Interpreting definitions • Which element is most likely to have an electron pulled off? • sodium • potassium • rubidium • Which element is most likely to pull shared electrons towards itself? • fluorine • chlorine • bromine