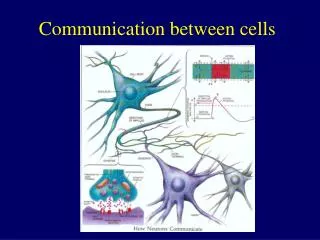
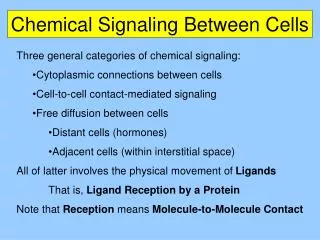
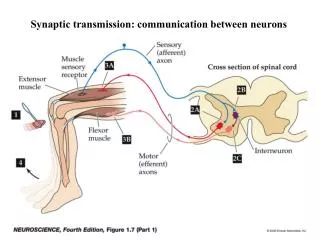
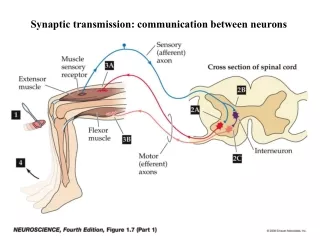
Communication between cells
210 likes | 404 Vues
Communication between cells. Electrical equivalent. Biology. R. I 2. I 1. I. I = I 1 + I 2. Nernst Equation. The Nernst equation relates the potential difference to the concentration difference in equilibrium: C i / C o = exp { - Z e (V i -V o )/kT } or

Communication between cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Electrical equivalent Biology R I2 I1 I I = I1 + I2
Nernst Equation The Nernst equation relates the potential difference to the concentration difference in equilibrium: Ci / Co = exp { - Z e (Vi -Vo )/kT } or Vi - Vo = (kT/Ze) ln (Co/Ci) with e = charge electron Z = valence of ion k = Boltzmann constant T = temperature Ci (Co) = concentration inside (outside) membrane
Example of Nernst equation t=0 t >> 0 R+ 50 Na+ 50 Cl- 100 Na + 100 Cl- 100 R+ 50 Na+ 64 Cl- 114 Na+ 86 Cl- 86 ΔV = 0 ΔV = - 10 If both Na and Cl, but not R+ can migrate through the membrane.
Problems with Nernst equation • considers only a single ion. • If multiple ions are involved, it assumes equal permeability for all ions • Applies only to passive transport • ions migrate independently of each other
Goldman/Hodgkin/Katz equation The Nernst equation relates the potential difference to the concentration difference in equilibrium for a single neuron. When several ions are involved, we obtain for equilibrium : Pk [K]o+PNa[Na]o+PCl[Cl]i ΔV = (RT/F) ln --------------------------------- Pk [K]i+PNa[Na]i+PCl[Cl]o with Pi = permeability of ion i [K]i/o = concentration inside/outside F = Faraday constant T = temperature ΔV = potential difference across membrane
0 mV outside V mV inside Hodgkin & Huxley: Current through an ion-channel 0 mV R I I Vion V mV Ohm’s law Conductance G=1/R Conductance G is a product of maximal conductance gCa and the fraction of open channels m3h
Gating kinetics State:
Gating kinetics Open State:
Gating kinetics m Open Closed State: m m (1-m) Probability: m m
V (mV) Gating kinetics m Open m m Closed State: m m (1-m) Probability: m m Channel Open Probability:
-3 x 10 1 8 t 0.8 (V) m (V) 6 m ¥ 0.6 (s) 4 m t 0.4 2 0.2 0 0 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 1.2 10 1 8 h (V) t (V) ¥ h 0.8 6 (s) h t 0.6 4 0.4 2 0.2 0 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 -100 -50 0 50 100 V (mV) V (mV) clamp clamp Parameter fitting (2)
-3 x 10 1 8 t 0.8 (V) m (V) 6 m ¥ 0.6 (s) 4 m t 0.4 2 0.2 0 0 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 1.2 10 1 8 h (V) t (V) ¥ h 0.8 6 (s) h t 0.6 4 0.4 2 0.2 0 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 -100 -50 0 50 100 V (mV) V (mV) clamp clamp Parameter fitting (2)
V (mV) Gating kinetics m Open m m Closed State: m m (1-m) Probability: m m gm(t) = gm, max(m∞ - m0)(1 - e-t/τ) gh(t) = gh, max(h∞- h0)e-t/τ gm gh g Channel Open Probability: m3h gNa time
Membrane voltage equation 0 mV 0 mV INa IC V mV V mV INa = gmax, Nam3h(V- VNa) Kirchoff’s law: -Cm dV/dt = gmax, Nam3h(V-Vna) + gmax, K n4 (V-VK ) + g leak(V-Vna)