Bacteriorhodopsin
350 likes | 894 Vues
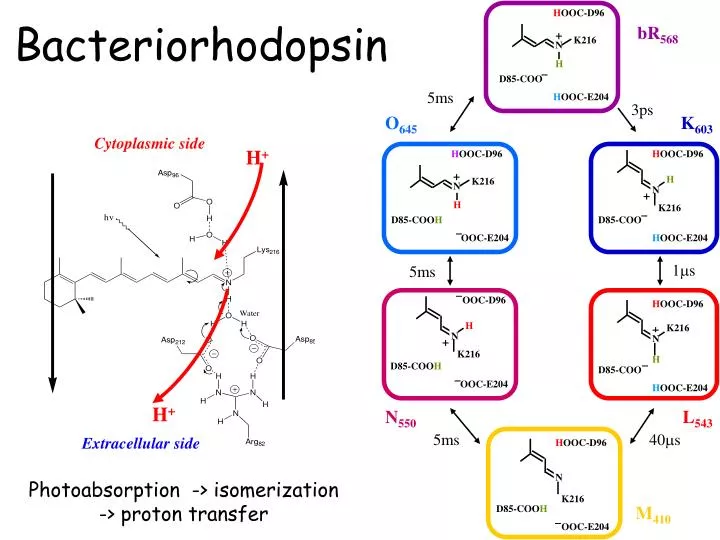
H +. H +. H OOC-D96. bR 568. +. K216. N. H. D85-COO. 5ms. H OOC-E204. Bacteriorhodopsin. 3ps. O 645. K 603. Cytoplasmic side. H OOC-D96. H OOC-D96. +. H. K216. N. N. +. H. K216. D85-COO H. D85-COO. OOC-E204. H OOC-E204. 1m s. 5ms. OOC-D96. H OOC-D96. H. +. K216.

Bacteriorhodopsin
E N D
Presentation Transcript
H+ H+ HOOC-D96 bR568 + K216 N H D85-COO 5ms HOOC-E204 Bacteriorhodopsin 3ps O645 K603 Cytoplasmic side HOOC-D96 HOOC-D96 + H K216 N N + H K216 D85-COOH D85-COO OOC-E204 HOOC-E204 1ms 5ms OOC-D96 HOOC-D96 H + K216 N N + K216 H D85-COOH D85-COO OOC-E204 HOOC-E204 N550 L543 5ms 40ms Extracellular side HOOC-D96 N Photoabsorption -> isomerization -> proton transfer K216 M410 D85-COOH OOC-E204
Chromophore-binding Pocket counterions Aromatic amino acids
Proton accessibility! + N H + H N cytoplasmic H+ photo-isomerization all-trans ~500 fs extracellular 13-cis
All structural details in the retinal chromophore are functionally important Protonated Schiff base Methyl groups conjugated backbone PA = EAH – EA b-ionone ring
Isomerization barriers in retinal Low barriers against double bond isomerization Ground state isomerization
A twisted chromophore in bR? 168° 165° 178° 177° 176° 177° • A twisted chromophore is also experimentally reported. • X-ray structures of bR report the twisted form of chromophore • The twist is found around the terminal double bonds • It may influence pKa of the chromophore
Photocycle of bR Photo-induced 5 ms 3 ps 1 ms 5 ms 40 ms 5 ms All intermediates are trapped in low temperature and have been characterized by vibrational and absorption spectroscopy.
Ultrafast spectroscopy 1 fs : 3 x 10-4 mm 1 ps : 3 x 10-1 mm
Ultrafast spectroscopy of bR 3 ps 5 ms 5 ms 1 ms 40 ms 5 ms Femtosecond time resolution H----I460----J625 Kobayashi et al., Nature, Nov 2001
Calculation of the Excited state Dynamics of Photoactive Molecules by ab initio Techniques Ab initio (First-Principles) dynamics of ethylene in vacuum Todd Martinez, Chemistry, UIUC LUMO 110 fs 50 fs 0 fs HOMO But what happens in the protein?
QM/MM calculations Lys216-RET O … MM N H N H MM QM QM H H … N H H QM dummy atom Asp85, 212 O O H O N QM MM
S1 S0 K BR C13=C14-trans C13=C14-cis Coupling of electronic excitation and conformational change in bR 13 7 9 11 15
+ N H + H N Hydrogen bond network in the retinal binding pocket T89 + K216 N O O Y185 H H H O O O H H D85 O D212 500 fs W402 O H O H W401 H H O O W406 H H Y57 + H N R82
Water movement after the photoisomerization T89 T89 all-trans D85 D85 D212 D212 Structure of the firstintermediate (1QKO.pdb) Structure of the ground state (1C3W.pdb) C13=C14 cis 13-cis 3 ps One water molecule is dislocated, but where is it?
T89 T89 T89 D212 D212 D85 D85 D212 D85 Early intermediates of bR’s photocycle 3ps 80ps BR K77K KL135K N-H: 270o (T89) N-H: 90o (D212) FTIR spec. (77K) X-ray (110K) (e.g., T89-D85: stronger) (W402 is dislocated, D85 is rotated) DEEX (kcal/mol) -4.0 (-1.8) -2.9 (-1.8)
Role of water in proton transfer QM/MM calculation proton transfer neutral zwitter -ionic energy (kcal/mol) Rearrangement of the hydrogen-bond network can induce the proton transfer. isomerization
Archaeal Membranes • Branched (less vulnerable to oxidation) • Etheric bridge, not esteric (less sensitive to hydrolysis) • Inverted glycerol stereochemistry Higher resistance to harsh conditions of their habitat: pH, heat, high salt and sulfur, …
MODELING OF THE INTEGRAL PURPLE MEMBRANE Bacteriorhodopsin trimer Internal water molecules Retinal chromophores Squalene molecules Intra-trimer lipids Bulk water Inter-trimer lipids
Charge distribution at different faces of the purple membrane Cytoplasmic Extracellular Basic :Acidic : Polar:Lipids
Kinetics of the photocycle is dependent on the lipid composition of the membrane We have 10 molecules of lipid per bR monomer PGP and squalene are necessary for the recovery of normal kinetics of the photocycle after detergent treatment of PM.
Helix dislocation at late stages of the photocycle Possible involvement of lipid-protein interaction in the photocycle