Energy Basics and the Laws of Thermodynamics
60 likes | 190 Vues
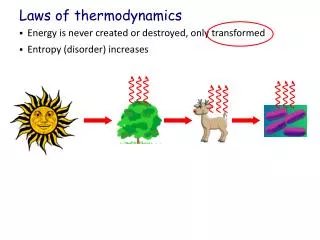
This educational content explores the foundational concepts of energy and thermodynamics. It defines energy as the capacity to perform work and relates it to matter, which cannot be created or destroyed (Law of Conservation of Matter). The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another. Various forms of energy are discussed, including potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, and nuclear energy, highlighting their characteristics and examples in real-world applications.

Energy Basics and the Laws of Thermodynamics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
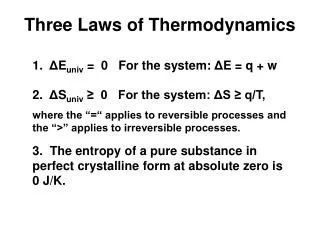
Part 1: Energy Basics • Define energyand matter? • Matter is stuff. • Energy is the capacity to take action and move matter around. 2. How are energy and matter related? • Energy moves matter. • Energy is stored in matter. 3. Restate the Law of Conservation of Matter? • Matter cannot be created or destroyed. 4. What is the First Law of Law Thermodynamics (the Law of Conservation of Energy)? • Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form into another.
Part 2: Various Forms of Energy • Mechanical Energy: The energy of movement or position. PE/KE • Potential Energy: Stored energy that is ready to be used due to an objects position or condition. For example, the energy stored in a spring, the stored energy of a rock on a ledge, the energy stored in the chemical bonds of two particles, the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom, and energy stored in a conductor of electricity. • Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion. The pattern of movement can be classified as random, wave, linear or rotational. For example, the energy of a thrown baseball, the energy carriedby vibrating particleslike sound. • Heat/Thermal Energy: The energy of moving particles that can change the temperature of something. For example, the heat you feel when you rub your hands together. KE • Light/Radiant Energy: The energy from electromagnetic waves. For example, light waves, solar radiation, radio waves, infrared radiation (lasers), microwaves, and x-rays. KE • Electrical Energy: This is the energy of electrons stored in or flowing through a conductor in a controlled motion. The flow of electrons is conducted through wires made of materials whose properties make this type of motion possible. For example, the energy transferred through electrical wires made of copper. KE • Chemical Energy: The energy stored in molecular bonds. This is the energy found trapped between the atoms that make up a given molecule. For example, photosynthesis - where the radiant energy from the sun is used to combine water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose sugar (C6H12O6) - most of the energy used is trapped within the bonds of the newly formed glucose. PE • Nuclear Energy: The energy stored in the nuclei of atoms. The energy can be released by: 1) radioactive decay: the spontaneous decay of large nuclei to smaller ones, which releases energy in the process; 2) fission: the purposeful breaking down of nuclei into smaller ones; 3) fusion: the process of small nuclei fusing together to make bigger ones. PE
Part 2: Various Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy The total energy an object has due to position, movement, or both Energy that is stored and ready to be used, due to an object’s position or condition. Potential Energy Energy that is released due to an objects movement or motion Kinetic Energy Examples: Examples: - Chemical - Electrostatic - Sound (wave) - Heat/Thermal (random) - Nuclear - Magnetic - Elastic - Gravitational - Electrical - Light/Radiant (wave) - Linear/Rotational Movement PE and KE are related b/c potential energy can be transformed into kinetic energy (and vice versa).
Part 3: Energy Transformations: First Law of Thermodyn. Device Initial Form of Energy Converted Form of Energy chemical electricity heat light nuclear Heat, electricity
Energy Transformation Demonstrations Energy cannot be created or destroyed. But, it can be transformed from one form to another. OBSERVE THE DEMONSTRATIONS: - Diagram the apparatus - Label the forms (and transformations) of energy - THE WAY THINGS GO