Private vs. Social Costs: Understanding Market Price Divergences and Their Implications
50 likes | 173 Vues
This analysis explores the divergence between private and social costs, highlighting how market prices often fail to reflect opportunity costs to society. It discusses reasons for these divergences, such as market failures, market power, externalities, public goods, and policy distortions. We delve into the market analysis of these issues, considering their effects on consumers, producers, government budgets, and third-party costs. Examples include commodity taxes, subsidies, and the impact of international trade on domestic markets.

Private vs. Social Costs: Understanding Market Price Divergences and Their Implications
E N D
Presentation Transcript
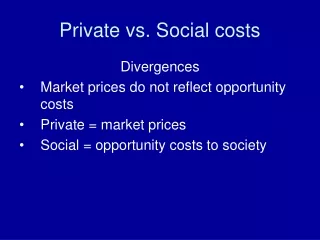
Private vs. Social costs Divergences • Market prices do not reflect opportunity costs • Private = market prices • Social = opportunity costs to society
Reasons for Divergences • Market Failures • Market power • Externalities • Public goods • Missing markets • Incomplete property rights • Distortions – result of policies that affect prices of commodities or factors • Commodity taxes/subsidies • Marketing restrictions/regulations • Taxes on economic activities • Etc.
Market analysis of divergences • Need to consider effects on • Consumers (CS) • Producers (PS) • Government budget (B) • External effects or third-party costs (EE)
Examples of market analysis • Market failures • Market power • Externalities • Market distortions (policies) • Domestic markets (no trade) • Commodity taxes/subsidies • Quantitative restrictions • International trade (small country) • International trade (large country)
Welfare Effects of Negative Externality CS0=abc PC0=dbg a Ss PS0=cbd EE0=0 m Sp CS1=akh b c P0 PC1=fhl h j k P1 PS1=khf EE1 =-dmhf ∆CS=+cbhk D ∆PS=+djhf - cbjk d ∆EE=-dmhf f g l ∆Net=-bmh Q0 Q1