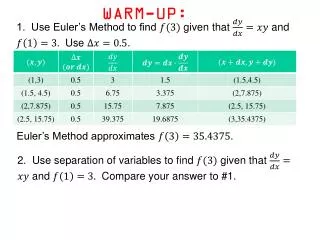
Warm Up
180 likes | 325 Vues
Warm Up . Match the following animals with their correct animal group: Animals: snake, squirrel, toad, eagle, rockfish Phylum: amphibian, bird, fish, mammal, reptile. Vertebrates. Vertebrates are animals with a backbone Body temperature

Warm Up
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm Up • Match the following animals with their correct animal group: Animals: snake, squirrel, toad, eagle, rockfish Phylum: amphibian, bird, fish, mammal, reptile
Vertebrates • Vertebrates are animals with a backbone • Body temperature • Endotherms – are able to maintain their body temperature (warm blooded) • Ectotherms – are not able to maintain their body temperature (cold blooded)
Fishy Fishy • Fish characteristics: • Fins – to propel, balance, and steer • Gills – an organ which removes oxygen from water (used for breathing) • Scales – protect the bodies of fish • Most reproduce externally – female lays eggs which are then fertilized by the male • Most are ectotherms (cold-blooded) • 3 Fish Types-cartilaginous, bony, and jawless
Types of Fish • Jawless • That’s right…. no jaws • Includes hagfish and lampreys • They eat dead fish or live as parasites • Cartilaginous • Skeleton is not bone – it is soft - cartilage • Includes sharks, rays, skates • Excellent hunters • Must constantly swim
Types of Fish • Bony Fish • These are most of the fish – 95% of all fish • Contain a “swim bladder”. Helps them maintain buoyancy. • Skeleton of bone
Amphibians – “double life” • Animals which can live on land and in water. • They have lungs for breathing • Eggs must stay moist. Hatch in water. • Ectotherms (cold blooded) – water helps maintain temperature. • Skin • is very thin. • They can absorb water through it….. And lose water through it. • Some absorb oxygen through skin • Some have poisons in skin • Different forms for young and adults • Metamorphosis – a change in form from juvenile to adult
Amphibians – “double life” • Salamanders • Live in woods • Much like prehistoric amphibians • Frogs and Toads • Make up 90% of all amphibians • Well adapted for land – strong legs, good ears, and strong vocal cords
Reptiles • All have lungs • Water tight skin – helps prevent dehydration. Skin very thick. • Body temperature • Ectotherms (cold-blooded) • Active when it is warm, less active when cold.
Reptiles- alligators, crocodiles, tortoises, turtles, snakes, and lizards • Eggs – have an amniotic egg • Hard shell – to protect and keep moisture inside • Large yolk- to nourish embryo • (Eggs can be laid under rocks, in the ground, in the desert)
Turtles and Tortoises • Turtles live in water (mostly) • Tortoises live on land. • Both lay eggs on land. • Crocodiles and Alligators • Live in water. Ferocious hunters. • Crocs – narrow head, pointed snout • Gators - broad head, round snout
Birds • Endotherms (warm-blooded) • Feathers around their body, scales on their feet. • Down – fluffy feathers, trap heat • Contour – stiff feathers, provide shape and help flying • Molting – shedding of old feathers • Lay eggs
Birds • High energy – • Fast digestion; some birds eat constantly. • Efficient respiration • Flying adaptations • Large eyes – see far distance • Rapid heart beat – to provide oxygen • Wing shape • Muscles – strong for flying • Hollow bones • Rigid skeleton – strong structure 4 Types of birds- flightless, water, prey, and perching (song)
Flightless birds Water birds Perching birds (song birds) Birds of Prey
Mammals • Specialized teeth– enables mammals to eat different types of food • Endotherms (warm-blooded) • Hair (or fur) helps trap heat • Fat – also helps insulate • Produce and provide milk for young. • Have lungs and a diaphragm to breath air. • Sexual reproduction – give birth to live young • Large brains
Types of Mammals • Placental mammals - young develop inside the mother’s body • Anteaters, moles, rodents, rabbits, bats, carnivores, trunk nosed mammals, hoofed mammals, cetaceans (dolphins), primates • Monotremes – lays eggs • Echidnas (pg 112) and platypus • Marsupials – give birth but young develop in pouch • Opossum, koalas, kangaroos
Activity- Part 1 • Create/fill in a concept map which shows the relationship between cold blooded vertebrates • Include these terms: reptiles, fish, amphibians, turtle ectotherms/cold blooded, alligator, frog, shark, metamorphosis, thick skin, gills, shell
Activity- Part 2 • Create/ fill in a concept map which shows the relationship between warm blooded vertebrates. • Include these terms: birds, mammals, milk, feathers, hair, monotremes, marsupials, placental mammals, platypus, endotherms/ warm-blooded, pouch, eggs, kangaroo, eagle, horse