Understanding DFS and Disk Quotas in Distributed File Systems
120 likes | 271 Vues
The Distributed File System (DFS) simplifies access to files distributed across a network, allowing users to view files as if they were located in one central location. DFS enables efficient management of shared folders by redistributing loads and ensuring uninterrupted access for users spread across multiple sites. Key DFS components include DFS roots, links, and targets. Additionally, disk quotas can be applied to NTFS-formatted drives to monitor and limit disk space for users, helping to control usage and prevent exceeding defined limits.

Understanding DFS and Disk Quotas in Distributed File Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
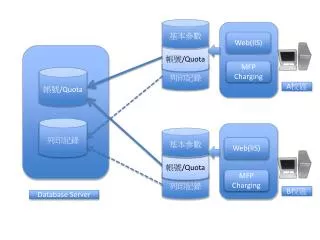
DISTRIBUTED FILE SYSTEM Distributed file system (Dfs) allows Administrators to make it easier for users to access and manage files that are physically distributed across a network. With Dfs, you can make files distributed across multiple servers. It may appear for Users that files actually reside in one place (computer) on the network.
Reasons 1. Users who access shared folders are distributed across sites. 2. Most users require access to multiple shared folders. 3. Server load balancing could be improved by redistributing shared folders. 4. Users require uninterrupted access to shared folders.
DFS Terms DFSROOT: DFS root is the beginning of a hierarchy of DFS links that points to shared folders DFSLINK: A link from a DFS Root to one or more Shared files or folders TARGETS: The Mapping destination of a DFS Root or Links which corresponds to a physical folder that has been shared
Topology Ring Topology
Topology Hub and Spoke Topology
Topology Full Mesh Topology
DISK QUOTA You can use disk quotas on drives formatted with the NTFS file system to monitor and limit the amount of disk space available to individual users. Disk quota tracks and control disk space usage for NTFS Partitions Prevent further disk space use and log an event when a user exceeds a specified disk space limit.