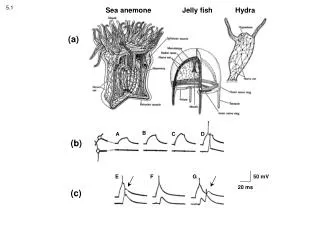
5.1
170 likes | 370 Vues
5.1. 前序 A B E F H I G C J K L D M N O Q P 后序 E H I F G B K L J C N Q O P M D A 层次 A B C D E F G J M H I K L N O P Q. 5.2. A. C. G. 将二叉树根结点作为有序树林第一棵树的根结点,循环处理 root=root->rchild ,依次将 root 所指结点作为其他树的根结点。 将上述方法施行于各树根结点的左子树。. B. E. F. D. 5.3. define MAXN 100

5.1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
5.1 前序 A B E F H I G C J K L D M N O Q P 后序 E H I F G B K L J C N Q O P M D A 层次 A B C D E F G J M H I K L N O P Q
5.2 A C G 将二叉树根结点作为有序树林第一棵树的根结点,循环处理root=root->rchild,依次将root所指结点作为其他树的根结点。 将上述方法施行于各树根结点的左子树。 B E F D
5.3 define MAXN 100 struct node { int data; struct node *lchild, *rchild; }; typedef struct node NODE;
if(t->lchild!=NULL ||t->rchild!=NULL) { p=t->lchild; t->lchild=t->rchild; t->rchild=p; } if(t->lchild!=NULL) stack[top++]=t->lchild; if(t->rchild!=NULL) stack[top++]=t->rchild; } } } 5.3 void exchange(t) NODE *t; { NODE *p, *stack[MAXN]; int top; if(t) { stack[0]=t; top=1; while(top>0) { t=stack[--top];
5.3 另解: NODE *change(t) NODE *t; { NODE *p; if(t==NULL) return(NULL); else { p=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); p->data=t->data; p->lchild=change(t->rchild); p->rchild=change(t->lchild); return(p); } }
while((top>0)&&(flag)) { t=stack[top-1]; if(t->rchild!=p) { t=t->rchild; flag=0; } else { printf(“%d “, t->data); top--; p=t; } } } 5.4 void hinderorder(t) NODE *t; { NODE *stack[MAXN], *p; int flag, top=0; while(top>0||t!=NULL) { while(t!=NULL) { stack[top++]=t; t=t->lchild; } p=NULL; flag=1;
5.5 (1)按前序遍历T′(略) (2)按中序遍历T′(略)
5.5 (3)中序遍历T′中无左子结点的结点 void f(t) NODE *t; { if(t!=NULL) { if(t->lchild==NULL) printf(“%d”, t->data); else f(t->lchild); f(t->rchild); } }
while(p!=NULL) { n++; p=p->rchild; } if((m=f1(t->lchild))>n) n=m; if((m=f1(t->rchild))>n) n=m; return(n); } 5.5(4)求T′中结点的左子结点本身和它的右下方子结点数的总数的最大值。 int f1(t) NODE *t; { NODE *p; int m, n; if(t==NULL) return(0); n=0; p=t->lchild;
5.6 struct node { char data; struct node *lchild, *rchild; } typedef struct node NODE;
j=0; while(b[j]!=a[i]) j++; if(top>0) if(j<s[top-1]) stack[top-1]->lchild=p; else { while((j>s[top-1])&&(top>0)) q=stack[--top]; q->rchild=p; } s[top]=j; stack[top++]=p; } return(root); } NODE *binatree(a,b,n) char a[ ], b[ ]; int n; { NODE *root,*p,*q,*stack[maxn]; int top, i, j, s[maxn]; if(n=0) return(NULL); top=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { p=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(node)); p->data=a[i]; p->lchild=p->rchild=NULL; if(n==1) return(p); else if(i=0) root=p;
5.8 int fully_tree(t) node *t; { if(t->lchild==NULL&&t->rchild==NULL) return(1); if(t->lchild!=NULL&&t->rchild!=NULL) if(fully_tree(t->lchild)) return(fully_tree(t->rchild)); return(0); }
p->data=tree[i].data; if(tree[i].rtag!=-1) stack[top++]=p; else p->rchild=NULL; q=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); if(tree[i].ltag==’0’) p->lchild=q; else { p->lchild=NULL; p=stack[--top]; p->rchild=q; } p=q; } p->data=tree[n-1].data; p->lchild=NULL; p->rchild=NULL; return(root); } 5.10 #define MAXN 100 typedef struct rnode { char data; char ltag; int rchild; } RNODE; typedef struct node { char data; struct node *lchild, *rchild; } NODE; RNODE tree[MAXN]; NODE *transfer(tree,n) RNODE tree[ ]; int n; { NODE *stack[MAXN],*root,*p,*q; int top, i; if(n==0) return(NULL); root=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); p=root; top=0; for(i=0;i<n-1;i++) {
5.11 #define MAXN 100 struct node { char data; int ltag, rtag; }; typedef struct node NODE; NODE s[MAXN];
m=0; for(j=i-1;j>=0;j--) { if(s[j].ltag==1) m++; if(s[j].rtag==0) m--; if(m==0) return(j); } } 5.11 int search_parents(s,n,a) NODE s[ ]; int n; char a; { int i, j, m; for(i=0;i<n&&s[i]!=a;i++); if(i=n) return(-1); if(s[i-1].ltag==0) return(i-1);
5.12 #include “stdio.h” struct node { char data; struct node *lchild, *rchild; int ltag, rtag; }; typedef struct node NODE; NODE *root;
p=p->lchild; else { while(p->rtag==1) p=p->rchild; if(p->rtag==0 &&p->rchild==NULL) break; p=p->rchild; } } } 5.12 void preorder(root) NODE *root; { NODE *p; if(root==NULL) return; p=root; while(1) { printf(“%c”,p->data); if(p->ltag==0 &&p->lchild!=NULL)